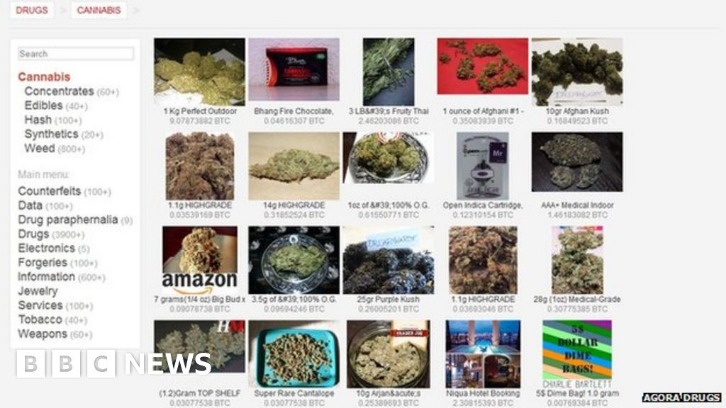
Common Structures of Dark Web Market URLs
Dark web market URLs typically exhibit specific structural patterns that facilitate secure and anonymous transactions. These URLs often use the “.onion” suffix, indicating their operation within the Tor network, which ensures user privacy and confidentiality. The structure of these URLs can vary, but they usually comprise a randomized string of characters followed by the “.onion” extension, making them difficult to predict or parse. For instance, some dark web markets use longer, complex addresses to add an extra layer of obfuscation. Understanding these common structures is crucial for navigating the dark web safely. For example, you might encounter URLs like dark web market URLs. Recognizing these patterns can help users identify legitimate sites and avoid potential scams or malicious links.

Typical Domain Formats
Dark web market URLs typically follow unique and recognizable structures that distinguish them from regular websites. These URLs are primarily designed to provide anonymity and security for users operating within the dark web environment. A common feature of these URLs is their use of specific domain formats that often include the “.onion” extension, indicating accessibility through the Tor network. These domain names tend to be alphanumeric strings that are difficult to memorize and are generated to ensure privacy. For example, a typical dark web market URL may appear as a long, randomized string of characters, often combined with a .onion suffix, making it unique and relatively secure against easy discovery.
Many dark web market URLs follow a standard structure that involves a primary domain followed by a path or subdirectory, which often contains further obfuscated or encrypted segments. This format helps organize different sections or categories within the marketplace while maintaining anonymity. The domain formats in these URLs are typically constructed with a focus on simplicity and security, emphasizing the need to hide the operator’s identity and location. Overall, the typical structure of dark web market URLs revolves around complex, non-memorable strings paired with the specialized .onion extension, creating a distinctive and secure URL format that is widely recognized within underground digital markets.
Use of Onion (.onion) and Hidden Services
Dark web market URLs typically have distinct structures that help users identify and access concealed marketplaces hosted on the Tor network. These URLs are designed to maintain the anonymity of both operators and visitors, often utilizing complex and unpredictable patterns to conceal their identities. Understanding the common structures of these URLs is essential for navigating the dark web securely and effectively.
One of the most prevalent features of dark web market URLs is the use of the .onion domain, which signifies that the website is accessible only through the Tor browser. These URLs are generated using a process that produces a unique cryptographic key, resulting in a seemingly random string of characters, often forming a 56-character address for v3 onion services. The typical structure involves a unique alphanumeric sequence followed by the .onion suffix, such as:
- Unique 56-character address + .onion: exemplifies the v3 onion addresses used in modern dark web markets and services.
These URLs frequently feature additional path elements or parameters for specific pages or categories within the marketplace, though the core address remains a cryptographically generated string. The design of .onion links prioritizes security and anonymity, making them difficult to predict or track.
In addition to onion addresses, dark web markets employ various hidden services that are accessible only through Tor, using specialized URL structures. These services include marketplace portals, forums, or private communication channels, all structured to obscure their locations from surveillance. The use of these URL structures ensures that the services remain resilient against censorship and shutdowns, thereby providing a resilient environment for illicit exchanges or discreet communications.
Overall, the common structures of dark web market URLs revolve around the cryptographically generated .onion addresses that serve as gateways to concealed marketplaces and services. Their unpredictable and secure design is fundamental to maintaining the anonymity and integrity of the dark web ecosystem, enabling users to access a wide range of hidden content safely. Recognizing these structures can assist in understanding how dark web markets operate and how they maintain their discreet nature.
Alternative TLDs and Domain Types
Dark web market URLs are unique addresses used to access illicit marketplaces hosted on the Tor network. These URLs are designed to provide anonymity for both users and operators, often employing specific structures and domain extensions that distinguish them from regular web addresses. Understanding the common structures of these URLs is essential for navigating or analyzing dark web markets effectively.
Typically, dark web market URLs use the .onion TLD, which is exclusively accessible via the Tor browser. These URLs often consist of a series of randomized alphanumeric characters, creating a complex and hard-to-guess address, for example, a URL like abc123def456…. This randomness helps enhance security and privacy. Some markets opt for shorter or more memorable URLs, but the majority follow a pattern of a long, pseudorandom string followed by the .onion extension.
In addition to the basic structure, there are alternative domain types and TLDs used within the dark web market ecosystem. Some operators might utilize specialized onion services with unique structures to enhance security or differentiate their platforms. There are also instances where .bitcoindark or similar pseudo-TLDs are used within private or less common networks for added obscurity.
- Common Structures:
- Long randomized strings: Most URLs consist of a complex string of characters, making them difficult to predict or link to other sites.
- Segmented URLs: Some marketplaces structure URLs with segments indicating specific categories or user zones.
- Subdomains: Rarely, some dark web URLs include subdomains to designate different sections or services.
- Alternative TLDs and Domain Types:
- .onion remains the standard for Tor-based dark web sites.
- Custom pseudo-TLDs, such as .bitcoindark, are sometimes employed for specific privacy or branding purposes within closed networks.
- Private or invitation-only markets may use less common domain structures to restrict access.
Recognizing these common URL structures and domain types is crucial for understanding how dark web markets are organized and how they maintain an element of secrecy in their online presence. The design of these URLs prioritizes security and anonymity, which are central to the dark web ecosystem.
URL Naming Conventions and Patterns
URL naming conventions and patterns play a crucial role in organizing and accessing dark web market sites securely and efficiently. Unlike conventional websites, dark web URLs often use complex, unique structures to enhance anonymity and resist detection. These patterns typically involve long, randomized strings of characters combined with the “.onion” suffix, which signifies access through the Tor network. Recognizing these URL patterns can assist users in identifying legitimate dark web market links and understanding the underlying organization of these clandestine platforms. For example, some dark web markets utilize specific URL structures that include consistent prefixes or suffixes, making it easier for users to remember or verify their destination. To explore various dark web market URLs, you can visit platforms such as this link for comprehensive browsing experiences.
Branding and Vendor Names in URLs
When navigating dark web markets, the structure and naming conventions of URLs play a crucial role in ensuring secure, memorable, and trustworthy access points. Proper URL patterns not only help users recognize legitimate marketplaces but also assist in maintaining consistency and safety across different platforms. Understanding these conventions can help users differentiate between reliable vendors and malicious actors operating within the dark web environment.
Dark web market URLs often follow specific patterns to facilitate branding and ease of access. These URLs typically incorporate clear branding elements or vendor names to foster brand recognition and credibility. For example, a marketplace may use a URL like darkmarketexample.onion to establish a strong identity, making it easier for users to find and remember the site. Vendor-specific URLs may also include the vendor’s name or unique identifier, which aids in direct navigation and reputation building within the community.
Common URL naming conventions in dark web markets include:
- Use of descriptive and memorable names that reflect the marketplace or vendor’s brand.
- Consistent URL patterns across various vendors and marketplaces to establish trustworthiness.
- Patterns that incorporate vendor-specific identifiers, sometimes in combination with category tags for quick browsing.
- Utilization of simple, clean URL structures to prevent confusion and facilitate easy access, especially on mobile devices.
Additionally, pattern recognition is critical for users to identify authentic market URLs amid the proliferation of imitation sites aiming to deceive users. Authentic dark web market URLs tend to follow predictable naming conventions that include clear branding, avoiding overly complicated or suspicious string patterns, which could indicate malicious intent.
In conclusion, effective URL naming conventions and patterns are essential components of branding efforts within dark web markets. They help create a recognizable identity for both platforms and individual vendors, facilitating trust and easy access. Recognizing common URL patterns also assists users in avoiding scams and ensuring they connect to legitimate sites. Whether browsing a dark web market or a vendor’s specific page, understanding these URL conventions can enhance security and streamline the user experience.
Randomized or Obfuscated URL Strings
- The seizure of Bitcoin and arrest of Ulbricht were meant to send a clear message to other cybercriminal enterprises.
- Here’s a look at several of the illegal items you can buy — with prices — courtesy of Privacy Affairs’s Dark Web Price Index 2023.
- It is considered a go-to site for malware purchasing, providing keyloggers, trojans, and other Malware as a Service products.
- Its commitment to privacy, diverse product offerings, and robust security measures make it a preferred choice for users seeking discreet transactions within the darknet.
URL naming conventions and patterns play a crucial role in the organization and accessibility of dark web market sites. These URLs often follow specific structures to ensure anonymity, security, and ease of access for users seeking to navigate hidden services. Dark web marketplaces commonly employ obfuscated or randomized URL strings to prevent easy detection and to protect both operators and users from potential authorities or malicious entities.
Randomized or obfuscated URL strings are a hallmark of dark web markets, serving as a protective measure against takedown attempts and surveillance. Instead of meaningful words, these URLs typically consist of a mixture of random characters, making it difficult for outsiders to predict or find the sites. For example, traditional market URLs might look like http://xxxxxx.onion, where the string is intentionally complex and non-descriptive. This pattern enhances security but can make navigation more challenging for regular users.
By employing such naming conventions, dark web market operators aim to reduce the risk of detection by law enforcement agencies. Additionally, using randomized URLs allows multiple markets to coexist within the same hosting environment without easily infringing on each other’s space or exposing patterns that might reveal their nature. These practices are an integral part of maintaining anonymity and operational security within the dark web ecosystem.
Overall, understanding URL patterns and naming conventions on the dark web highlights the importance of security and privacy considerations in these environments. Whether for legitimate or illicit purposes, the use of randomized and obfuscated URL strings underscores the ongoing effort to balance accessibility with protection from external threats.
Numerical and Alphanumeric Domain Names
URL naming conventions and patterns play a significant role in the organization and accessibility of dark web marketplaces. These URLs typically follow specific structures designed to enhance privacy and security for users and operators alike. On dark web markets, URLs are often composed of complex alphanumeric strings that serve as unique identifiers, making them difficult to predict or analyze easily. This approach helps minimize the risk of takedowns and enhances anonymity by avoiding easily recognizable keywords or patterns.
Numerical and alphanumeric domain names are common within these marketplaces, often consisting of random or semi-random strings that provide an additional layer of obfuscation. For example, a dark web market URL might appear as abc123xyz.onion or xyz987abc.onion. Such naming conventions serve to prevent easy association with specific services or products, making it challenging for authorities to track or block these sites. Consistent use of complex patterns helps maintain the resilience of dark web platforms despite external pressures.
Adopting unpredictable URL patterns is a strategic choice within the dark web ecosystem. These URLs often incorporate a combination of letters, numbers, and sometimes randomly generated characters, which ensures that each marketplace remains distinct and reduces the likelihood of detection. Additionally, some markets employ changing or rotating URLs that periodically generate new address patterns to further enhance security and operational continuity. Understanding these naming conventions provides insight into the resilience and adaptability of dark web markets and their emphasis on maintaining user anonymity.
Marketplace URL Accessibility and Navigation
Marketplace URL accessibility and navigation are critical elements when exploring dark web markets, where users seek secure and efficient methods to access various platforms. Ensuring that URLs are easy to find and navigate helps users seamlessly connect to legitimate dark web marketplaces while maintaining privacy and security. Clear pathways to URLs such as http://nexusafejew45osqaawl2xqjwmincsfvjwuwtm2fums2kjeon7tbmlid.onion facilitate smoother transactions and minimize confusion. Proper organization of dark web market URLs enhances user experience, fosters trust, and encourages safe browsing practices amidst the complexities of the hidden internet landscape.
Direct Links and Searchable Indexes
Accessing dark web market URLs requires careful consideration of accessibility and navigation strategies to ensure users can efficiently locate and utilize these platforms. These URLs are often designed to be direct and straightforward to facilitate quick entry for users familiar with the dark web environment. Providing clear, logical navigation pathways is essential for users to find specific services or products within the market, especially given the anonymous and discreet nature of these platforms. Ensuring that URLs are stable and easily shareable can significantly enhance usability and user trust.
Direct links serve as essential gateways to dark web marketplaces, allowing users to bypass complex navigation processes and reach their intended destination swiftly. These links should be well-maintained and periodically verified to prevent broken or outdated addresses, which can hinder access and reduce user confidence. For example, well-structured marketplace URLs that lead directly to specific categories or listings help streamline the browsing experience within these anonymous environments.
Searchable indexes also play a crucial role in the organization of dark web markets. These indexes enable users to search for products, services, or vendors within the marketplace efficiently. Because privacy is paramount in dark web activities, indexes are typically designed to be concealed or encrypted, accessible only through authorized channels. Ensuring these search functionalities work seamlessly, while maintaining anonymity, enhances overall accessibility. Proper categorization and indexing of items facilitate easier navigation and improve user experience within the marketplace ecosystem.
Referral and Affiliate URL Schemes
Ensuring the accessibility and clear navigation of marketplace URLs is essential for user experience and security, especially when dealing with dark web markets. These URLs often serve as gateways to sensitive and specialized platforms, making consistent accessibility vital for users seeking quick and reliable access. Proper structuring of marketplace URLs facilitates seamless navigation, allowing users to find products or services efficiently without confusion or unnecessary obstacles. Maintaining a straightforward URL scheme helps build trust and reduces the risk of phishing or malicious redirects, which are common security concerns on the dark web.
Referral and affiliate URL schemes play a significant role in dark web markets by enabling partnerships and incentivized link sharing. These schemes often use unique URL parameters to track referrals, commissions, or traffic sources across different dark web marketplaces, such as DarkMarket or Silk Road. Clear and secure URL schemes ensure that affiliates and partners can efficiently refer users without compromising privacy or security. Properly designed URLs also help prevent misuse, including link hijacking or unauthorized access, by incorporating secure tokens or encryption techniques in the URL structure.

Overall, attention to URL accessibility, navigation, and scheme security is crucial for the integrity and usability of dark web marketplaces. Well-structured marketplace URLs foster trusted environments for users while supporting effective referral systems. Such best practices mitigate risks associated with malicious activities and improve the overall experience for participants engaged in these discreet online activities.
Marketplace Directory Listings and Aggregators
Ensuring marketplace URL accessibility and seamless navigation is crucial for maintaining user trust and facilitating efficient browsing in any online marketplace, including those operating on the dark web. Clear and consistent URL structures help users easily locate and access specific markets or listings, which is particularly important in dark web environments where security and anonymity are prioritized. Properly organized marketplace directory listings assist users in discovering relevant categories and vendors, promoting transparency and accountability. Aggregators play an essential role by consolidating listings from multiple dark web markets such as darkmarketwxyz or hiddenmarketabc, offering a centralized platform for users to compare and access various services securely. Ensuring that URLs are accessible, well-structured, and navigable enhances overall user experience while maintaining the necessary anonymity and security features inherent to dark web markets.
Security Features of Dark Web Market URLs
Dark web market URLs are specialized addresses used within the dark web to access various marketplaces that often deal with a wide range of goods and services. Due to the illicit nature of many of these platforms, security features are critically important to protect users from potential threats such as surveillance, hacking, and identity theft. These URLs typically employ advanced security measures like encryption, anonymization, and encryption protocols to ensure user privacy and safety. For example, some dark web market URLs, like Nexusafe Junction, incorporate multiple layers of security to safeguard transactions and personal data. Understanding how these security features function is essential for navigating the dark web responsibly and securely.
Encrypted and Secured Protocols
Dark web market URLs are specialized web addresses used to access hidden online marketplaces that operate within the dark web. Security features surrounding these URLs are vital for protecting users from malicious activities and maintaining anonymity. These marketplaces often utilize encrypted and secured protocols to ensure that communications between users and the marketplace are private and resistant to interception or tampering. The use of encrypted protocols, such as TLS (Transport Layer Security), helps safeguard data transmitted during transactions and browsing sessions, reducing the risk of hacking or eavesdropping.
Dark web market URLs typically employ the Tor network, which assigns them a special domain ending in “.onion.” These onion URLs are only accessible via Tor browsers, which provide an added layer of security through routing traffic through multiple relays, thus anonymizing user identities. This layered routing mechanism makes it significantly more difficult for third parties to trace users or the location of the marketplace itself. Additionally, various dark web marketplaces implement security features like two-factor authentication, encrypted messaging, and multisignature wallets to further protect user data and transaction integrity.
The combination of secure protocols, encrypted communications, and anonymous access methods ensures that dark web market URLs remain obscured from surveillance and unauthorized monitoring. These security measures are essential for maintaining user privacy, safeguarding sensitive information, and providing a safer environment for transactions within the dark web. Overall, the robust security infrastructure surrounding dark web market URLs underscores the importance of encryption and secure protocols in preserving anonymity and integrity in this shadowy digital space.
Use of VPNs and Anonymization Techniques
The security features of dark web market URLs are designed to provide users with a layer of anonymity and protection from potential threats. These URLs often utilize specialized domain names and static structures to prevent easy tracking and linking back to users or operators. Dark web market URLs typically employ a unique “.onion” or similar anonymous domain, which requires specific access methods such as the Tor network. This setup helps shield user identities and location data from surveillance or malicious entities. Additionally, these URLs are frequently updated or modified to avoid detection or blocking by authorities, ensuring continued access for users.
To enhance security further, users often rely on VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and anonymization techniques when accessing dark web market URLs. VPNs hide a user’s IP address by routing internet traffic through encrypted servers in different locations, adding an extra layer of privacy. When combined with the Tor network, VPNs significantly reduce the risks of monitoring or tracing activities. Anonymization techniques also include the use of secure browsers, proxy servers, and operational security practices such as avoiding personal information disclosure and employing pseudonymous identities. Employing these methods creates a robust barrier against potential cyber threats, surveillance, and law enforcement tracking when navigating dark web marketplaces.
Mirror Sites and Dynamic URL Generation
The dark web market URLs are designed with several security features to help protect user privacy and ensure safe transactions within the hidden marketplace environment. These URLs often utilize complex structures, such as mirror sites, to maintain accessibility even if the main site is taken down or blocked. Mirror sites replicate the original marketplace, providing users with alternative access points without revealing their true locations, thereby enhancing security and resilience against censorship or shutdown efforts.
Dynamic URL generation is another common security feature employed by dark web markets. Instead of static URLs that remain constant and can be easily tracked or blacklisted, these sites generate new URLs periodically or after each session. This practice makes it more challenging for monitoring agencies or malicious actors to locate and shut down specific marketplaces, safeguarding user activity and maintaining market availability.
Additionally, dark web market URLs often incorporate obfuscated or encrypted parameters, adding an extra layer of security to prevent easy identification or targeting. These measures, along with the frequent use of mirror sites and dynamic URL changes, work collectively to protect both vendors and buyers, ensuring the continued operation and anonymity crucial to dark web marketplaces.