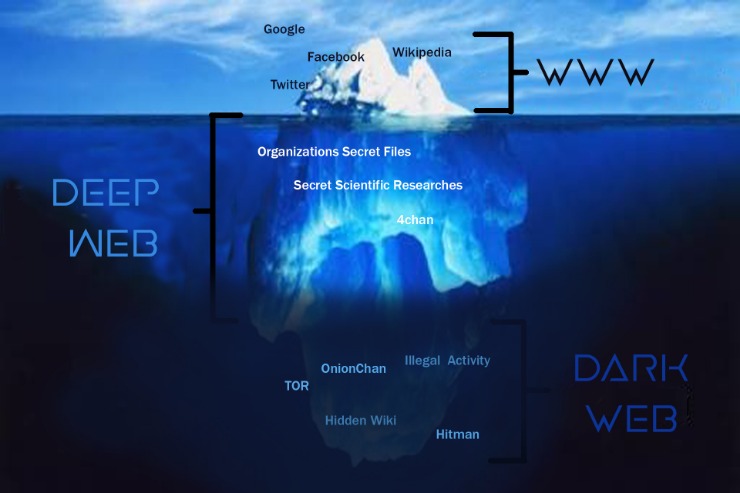
Overview of Dark Marketplaces
The dark marketplaces, often referred to as dark markets, are hidden online platforms that facilitate the exchange of goods and services outside the reach of traditional law enforcement and regulatory authorities. These marketplaces operate on the dark web, utilizing encrypted networks to maintain anonymity for both buyers and sellers. While some are legitimate venues for privacy-focused transactions, many are notorious for hosting illegal activities such as the trade of contraband, stolen data, and illicit services. Understanding the structure and operations of darkmarket platforms is essential for cybersecurity professionals, law enforcement agencies, and individuals interested in digital privacy. Exploring secure and anonymous marketplaces, such as darkmarket, provides insight into the complexity of these hidden online economies and their impact on global digital security.

Types of Dark Web Markets
The dark web hosts a variety of marketplaces collectively known as darkmarkets, which operate outside the reach of traditional internet search engines and law enforcement. These clandestine platforms provide a space for the exchange of goods and services that are often illicit in nature, ranging from drugs and weapons to stolen data and counterfeit documents. Darkmarkets are characterized by their anonymity features, such as the use of cryptocurrencies and anonymizing networks, which help both buyers and sellers maintain privacy and evade detection.
There are several types of dark web markets, each specializing in different categories of products or services. General marketplaces host a broad range of items and facilitate various transactions, often acting as a hub for multiple vendors. Niche marketplaces focus on specific categories like hacking tools, counterfeit currency, or illegal pharmaceuticals, catering to particular demand segments. Additionally, some darkmarkets operate on a peer-to-peer basis, enabling direct exchanges between individuals without a centralized middleman, which can sometimes enhance privacy and reduce the risk of law enforcement infiltration.
Despite their secretive nature, darkmarkets are a significant concern for cybersecurity and law enforcement authorities worldwide due to their involvement in illegal activities. Understanding the different types of dark web markets helps in developing strategies for detection, disruption, and prevention of criminal operations facilitated by these platforms.
Categories of Illicit Activities
Dark marketplaces, often referred to as darkmarkets, are online platforms that operate on the dark web, providing a hidden environment where users can buy and sell a wide range of goods and services. These marketplaces are characterized by their anonymity features, making it difficult for authorities to track transactions and identify participants. The secrecy and unregulated nature of darkmarkets attract various illicit activities, turning them into hubs for illegal trade across the globe.
Within darkmarkets, several categories of illicit activities flourish, driven by the demand for illegal goods and services. These include the sale of narcotics, counterfeit items, stolen data, and other prohibited products. The presence of these activities underscores the importance of understanding the risks and legal implications associated with engaging in such marketplaces.
- Narcotics and controlled substances
- Counterfeit currencies and documents
- Stolen financial and personal data
- Illegal weapons and firearms
- Malware and hacking tools
- Fake identification and credentials
- Unlicensed pharmaceuticals and health products
- Pirated digital content such as movies, music, and software
Law enforcement agencies worldwide continue to monitor darkmarkets in their efforts to combat illegal activities. However, the inherent anonymity and encryption technologies used by these platforms pose significant challenges. The presence of these illicit categories within darkmarkets highlights the ongoing need for awareness, cybersecurity measures, and legal action to mitigate the harms associated with such illegal transactions.
Common Goods and Services on Dark Markets
Dark markets have become an infamous part of the digital landscape, serving as underground platforms where a variety of goods and services are exchanged outside traditional legal channels. These anonymous online marketplaces often facilitate transactions involving both legal and illegal items, ranging from pharmaceuticals and digital currencies to hacking services and counterfeit documents. The complex nature of these platforms makes understanding the types of common goods and services offered crucial for comprehending their impact on online security and law enforcement efforts. For those interested in exploring more about the darkmarket ecosystem, additional resources are available to offer insights into its operational dynamics and the risks involved.
Illegal Substances and Drugs
Dark markets, often operating within the shadowy corners of the internet, serve as clandestine platforms where a wide array of goods and services are exchanged outside the purview of legal authorities. Among the most common offerings on these platforms are illegal substances and drugs, which attract a significant portion of users seeking anonymity and convenience. These underground marketplaces facilitate the purchase and sale of narcotics, including opioids, stimulants, and hallucinogens, often with discreet payment methods such as cryptocurrencies.
In addition to drugs, dark markets also feature various other illicit goods and services, including stolen data, counterfeit documents, hacking tools, and malware services. The anonymity provided by encryption technologies and cryptocurrencies enables vendors and buyers to operate without revealing their identities, making it difficult for law enforcement agencies to track and shut down these operations.
Despite the illegality surrounding these transactions, their prevalence highlights a demand-driven economy that thrives in the shadows. The sale of illegal substances on dark markets poses serious public health risks, contributing to addiction, overdose, and the spread of diseases. Authorities worldwide continue to develop strategies to combat these activities, yet the resilience and adaptability of dark market ecosystems complicate enforcement efforts.
Understanding the dynamics of dark markets and their common goods is essential for developing effective countermeasures. These platforms not only undermine legal frameworks but also facilitate the proliferation of dangerous substances and services that can have profound social and health impacts. Ongoing efforts seek to curb these illegal activities while balancing the need for privacy and security in digital spaces.
Counterfeit and Fake Identification
Dark markets, often accessed through specialized anonymous networks, are known for facilitating the exchange of a variety of goods and services outside the boundaries of legal commerce. These platforms have gained notoriety for offering items that are typically prohibited or heavily regulated in the mainstream market, including counterfeit products and illegal services. Within these dark markets, buyers and sellers often operate in a clandestine environment, making it challenging for authorities to monitor and enforce laws effectively.
One prevalent category of goods on dark markets includes counterfeit and fake identification documents. These items range from forged passports and driver’s licenses to fake visas and identification cards. Such documents are in high demand for individuals seeking to bypass security measures, or for those involved in illicit activities. The production and sale of fake IDs on these platforms are often carried out by specialized vendors who utilize sophisticated printing techniques, making it increasingly difficult to distinguish the counterfeit from genuine identification.
Aside from counterfeit IDs, dark markets also frequently offer a variety of other illegal goods, including illicit drugs, stolen data, and unregulated pharmaceuticals. The availability of counterfeit goods and fake identification fuels various criminal activities, such as identity theft, fraud, and immigration violations. Participants in dark markets often prioritize anonymity, using encrypted communication channels and digital currencies to conceal their identities and transactions.
Despite efforts by law enforcement agencies worldwide, the operation of dark markets continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and the persistent demand for illegal goods and services. As a result, understanding the common offerings on these platforms, like counterfeit and fake identification documents, is essential for developing effective strategies to combat illegal activities and protect individuals and institutions from associated risks.
Weapons and Hacking Tools
The dark market environment has become a hub for the exchange of various goods and services that are often illegal or heavily regulated in mainstream markets. Among the most common offerings are goods and services related to weapons and hacking tools, which pose significant concerns for law enforcement and cybersecurity communities. These markets operate in the shadows of the internet, primarily accessed through hidden networks that provide anonymity to buyers and sellers.
Weapons sales on dark markets typically include firearms, ammunition, and sometimes explosives, often sourced from regions with lax regulations or illegal manufacturing. The availability of such items raises alarms due to their potential use in criminal activities and acts of violence. Additionally, the distribution of hacking tools is increasingly prevalent, enabling cybercriminals to conduct activities such as data breaches, financial theft, and ransomware attacks with relative ease. These tools include malware, phishing kits, and remote access trojans, which are frequently marketed to a wide audience seeking to exploit digital vulnerabilities.
The exchange of these goods and services on dark markets is facilitated through cryptocurrencies, which provide a level of financial privacy. The anonymity and untraceability offered by these platforms complicate enforcement efforts, making it difficult to track and dismantle illegal operations. The proliferation of weapons and hacking tools on these markets underscores the importance of international cooperation and cybersecurity measures to combat their spread and prevent potential harm to individuals and societies.
Stolen Data and Personal Information
Dark markets, also known as dark web marketplaces, are digital platforms that facilitate the exchange of goods and services outside the reach of traditional online commerce. These markets are often accessed through anonymizing tools, allowing users to conduct transactions with a high degree of privacy. One prevalent aspect of dark markets involves the trade of common goods and services that range from illicit substances to counterfeit products. These platforms serve as hubs where vendors and buyers can connect under pseudonyms, making detection and regulation challenging for authorities.
Among the most concerning activities on dark markets is the sale of stolen data and personal information. Cybercriminals exploit these platforms to distribute compromised login credentials, social security numbers, financial information, and other sensitive data. Such stolen information is highly valuable and can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, and various other malicious activities. The anonymity provided by dark markets enables cybercriminals to sell and purchase stolen data with minimal risk of detection, fueling a thriving underground economy.
The trade in stolen data and personal information has significant implications for individuals and organizations alike. Victims often face financial loss, reputational damage, and a lengthy process to regain control of their compromised data. Moreover, the sale of such information on dark markets underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity practices and data protection measures. Efforts to counteract these illegal exchanges involve international cooperation and advanced detection techniques, but the concealed nature of dark markets makes eradication a persistent challenge.
Mechanisms and Features of Dark Markets
Dark markets, also known as darknet marketplaces, are online platforms that operate within the hidden parts of the internet, facilitating the anonymous exchange of goods and services. These markets leverage sophisticated mechanisms to ensure privacy and security for both buyers and sellers, often employing encryption technologies, cryptocurrencies, and Tor network access. Key features of dark markets include encrypted communication channels, decentralized transaction methods, and the use of escrow services to reduce the risk of fraud. Understanding the mechanisms behind these platforms reveals how they maintain their covert operations and attract illicit trade. For those interested in exploring more about the intricacies of these clandestine networks, the darkmarket offers a comprehensive landscape of their features and functionalities.
Marketplace Structures and Bidding Systems
Dark markets, often referred to as darknets or hidden marketplaces, operate within a concealed layer of the internet that requires specialized access methods, such as TOR or I2P networks. These platforms are designed to facilitate anonymous trading of various goods and services, often including illicit items, while prioritizing user privacy and security. The underlying mechanisms of dark markets rely heavily on encryption and anonymization technologies to protect both buyers and sellers from detection and law enforcement investigations.
One key feature of dark markets is their marketplace structure, which typically involves decentralized or semi-centralized systems. Unlike traditional online marketplaces, dark markets often utilize peer-to-peer architecture, where transactions are directly negotiated between parties through encrypted channels. They may also incorporate escrow services, where funds are held securely until both parties fulfill their contractual obligations, adding a layer of trust in an otherwise risky environment. The platforms usually feature extensive verification processes, though these can vary significantly depending on the specific marketplace.
Bidding systems are a common mechanism employed on dark markets to facilitate fair trading and price discovery. Sellers may list items with an asking price, or alternatively, buyers can engage in bidding or negotiation, allowing prices to fluctuate based on demand and supply dynamics within the marketplace. These systems often include reputation or review mechanisms to establish credibility, with transparent feedback loops influencing future transactions. Advanced dark markets also implement automated or algorithm-based bidding systems, which can optimize pricing and improve market efficiency. Overall, these features contribute to creating a complex, resilient ecosystem that sustains illegal trade activities while maintaining user anonymity.

Payment Methods: Cryptocurrency and Anonymity
Dark markets operate as clandestine online platforms where illicit goods and services are exchanged, often evading traditional law enforcement oversight. A core aspect of these markets is their reliance on sophisticated mechanisms to maintain user anonymity and secure transactions. Understanding the features and payment methods employed, particularly cryptocurrencies, is essential to grasp their operational dynamics.
One of the defining features of dark markets is their use of advanced anonymity protocols. These platforms often employ encryption techniques and decentralized architectures to prevent unauthorized tracking and surveillance. This focus on privacy ensures that both buyers and sellers can operate with a reduced risk of exposure, fostering an environment where illicit trade can flourish.
Regarding payment methods, cryptocurrencies are the primary financial instruments utilized within dark markets. Digital currencies such as Bitcoin, Monero, and other privacy-focused coins enable users to conduct transactions without revealing personally identifiable information. Cryptocurrency transactions offer a level of pseudonymity and security that traditional payment methods cannot provide, making them ideal for underground trade.
- Cryptocurrency: The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies allows for international and seamless transactions, bypassing conventional banking systems that could impose restrictions or traceability. Monero, in particular, is favored for its enhanced privacy features, which obscure transaction data and participant identities.
- Anonymity Features: Dark markets often incorporate additional security measures such as multisignature wallets, decentralized escrows, and use of coin mixers or tumblers. These features complicate the tracing of funds and enable users to maintain higher levels of anonymity.
Overall, the combination of encrypted communication channels, privacy-preserving cryptocurrencies, and secure transaction mechanisms forms the backbone of dark market operations. These features collectively enable anonymous and often untraceable exchanges, posing ongoing challenges for law enforcement agencies worldwide. As technology advances, dark markets continue to adapt their mechanisms to enhance privacy and security, perpetuating their role in underground economies.
Regionalization and Language Localization
Dark markets, also known as darknets or darknet markets, are clandestine online platforms that facilitate the exchange of goods and services, often involving illegal or ethically questionable items. These markets operate within the hidden layers of the internet, primarily accessed through anonymization tools like Tor, which help conceal user identities and locations. Understanding the mechanisms and features of these markets is essential for grasping their role in the digital underground economy.
One of the key features of dark markets is their reliance on encryption and anonymization technologies to maintain security and privacy for users. Blockchain and cryptocurrency transactions are prevalent to facilitate anonymous payments, making traceability difficult for law enforcement agencies. Marketplaces often implement escrow services, where funds are held until both buyer and seller confirm the transaction’s completion, thereby reducing fraud risk.
Regionalization plays a notable role in dark markets, with some platforms catering specifically to certain geographic regions or linguistic groups. This segmentation ensures localized language support, currency options, and region-specific regulations, which can enhance user trust and facilitate smoother transactions. Such regional customization also allows vendors to target specific markets more effectively, increasing their chances of successful sales.

Language localization is another critical feature to attract a diverse user base in dark markets. Platforms often provide multilingual interfaces, allowing users to navigate and conduct transactions comfortably in their native language. Language support is vital for user engagement, reducing misunderstandings and increasing transaction efficiency. It also helps in building trust within different communities, fostering a sense of familiarity and security.

In summary, dark markets employ sophisticated mechanisms such as encryption, cryptocurrency, and escrow services to maintain anonymity and security. Regionalization and language localization further enhance their accessibility and attractiveness by catering to specific user demographics, facilitating more effective and discreet trading within these covert online environments.
- In 2024, the platform grew significantly in popularity, partly because of its strategic acquisition of users from a number of recently shut-down marketplaces, such as AlphaBay and Incognito Market, which had recently closed their doors.
- Learn effective strategies for conducting threat hunting in your organization.
- Established in 2022, Torzon market is one of the biggest and most diverse marketplaces on the dark web.
- Patterns recommended to avoid include hiring hitmen like Dread Pirate Roberts, and sharing handles for software questions on sites like Stack Exchange.
- As a show of appreciation, the Council offered him the chance to join their organization.
Evolution and Trends in Dark Markets
The landscape of dark markets has experienced significant evolution and shifting trends over recent years, reflecting broader changes in technology, law enforcement tactics, and user behavior. As digital anonymity becomes both more sophisticated and more challenged, new platforms emerge while others decline or adapt their methods of operation. The darkmarket ecosystem continues to be a complex environment where illicit transactions and gray-area activities thrive, often mirroring legitimate online marketplaces but operating under the radar. Understanding these trends is essential for staying informed about the risks and developments within this clandestine sphere.
Emergence of New Platforms in 2024
The landscape of dark markets has been continuously evolving, reflecting technological advancements and shifting legal landscapes. In 2024, we observe significant trends shaping this clandestine ecosystem, driven by both innovation and increased efforts to combat illicit activities. Dark markets, often associated with anonymous transactions and unregulated platforms, are rapidly adapting to new challenges and opportunities in the digital realm.
One notable trend in 2024 is the emergence of more sophisticated anonymity tools and privacy-focused platforms that facilitate secure transactions beyond traditional cryptocurrency channels. These platforms are leveraging advanced encryption technologies and decentralized architectures to minimize traceability, making law enforcement efforts more complex. The proliferation of such platforms indicates a shift towards more resilient and user-centric dark market environments.
Furthermore, new platforms are increasingly incorporating automation and artificial intelligence to streamline transactions and enhance user security. This not only improves operational efficiency but also complicates efforts to monitor and shut down illicit marketplaces. The integration of AI also raises concerns about enhanced scam mechanisms, misinformation, and malicious activities within dark markets.
Additionally, the diversification of offerings on dark markets is evident in 2024, with a broader range of illegal goods, including pharmaceuticals, stolen data, and counterfeit products. The evolution of *darkmarket* platforms caters to diverse illicit demands, further embedding these channels into the shadow economy. As these markets evolve, they also adopt more resilient payment systems and escrow services to build user trust and reduce fraud.
Overall, the trend toward decentralization, technological innovation, and diversification signifies a dynamic and adaptive dark market environment in 2024. Understanding these ongoing changes is crucial for cybersecurity professionals, policymakers, and law enforcement agencies working to mitigate the risks posed by these clandestine platforms.
Law Enforcement Disruptions and Market Shutting
The landscape of dark markets has evolved significantly over the past decade, reflecting shifts in technology, law enforcement tactics, and user behavior. Originally emerging as clandestine spaces for anonymous trade, these markets have become more sophisticated, utilizing cryptocurrencies and anonymizing networks to bypass traditional financial and legal systems. This progression has made it challenging for authorities to track illicit transactions and disrupt operations effectively.
Recent trends indicate an increase in the use of decentralized and peer-to-peer platforms, which further complicate law enforcement efforts. These platforms often emphasize privacy and security, making investigations more complex. Moreover, the frequent appearance of new markets, combined with the shutdown of older ones, illustrates a continual cycle of emergence and suppression. Law enforcement agencies around the world have ramped up their efforts, employing advanced cyber forensics, undercover operations, and international cooperation to dismantle key players.
Market shutdowns tend to result from successful investigations or disruptions targeted at major vendors or infrastructure providers within the darkmarket ecosystem. However, these closures often lead to the rise of new marketplaces that adopt more resilient technologies or different operational strategies. This ongoing cat-and-mouse game underscores the resilience and adaptability of darkmarkets, which persist despite concerted enforcement efforts.
As the landscape continues to shift, understanding the evolving nature of darkmarkets and law enforcement responses is crucial for developing effective policies and security measures. Monitoring these trends helps stakeholders anticipate future challenges and adapt strategies to mitigate illicit activities while respecting legal boundaries and privacy concerns.
Market Adaptations: Exit Scams and Resilience
Dark markets have undergone significant evolution over the past decade, adapting rapidly to technological advancements and law enforcement efforts. Initially emerging as underground platforms for the exchange of illicit goods, these markets have become more sophisticated, leveraging secure communication protocols and cryptocurrencies to facilitate anonymous transactions. The dynamic nature of dark markets reflects their capacity for resilience despite persistent legal crackdowns and efforts to dismantle them.
Market adaptations such as exit scams—where operators abruptly shut down and abscond with users’ funds—highlight both the vulnerabilities and strategic shifts within these spaces. These scams, while damaging to users, often serve as a form of revolution within the ecosystem, prompting the creation of improved security measures and decentralized platforms aimed at minimizing such risks. The resilience of dark markets can be observed in their ability to recover and re-emerge swiftly after shutdowns, often under new management or with enhanced operational protocols.
Technological innovations continue to influence trends in dark markets, including the adoption of decentralized marketplaces, enhanced anonymity features, and improved escrow services that aim to verify trustworthiness between parties. Such advancements not only bolster the security and usability of these platforms but also complicate efforts by authorities to detect and disrupt illicit activities. As a result, dark markets remain a resilient and adaptive component of the underground economy, reflecting broader trends in digital privacy and cryptocurrency usage.
Cybercriminal Operations and Impact
Cybercriminal operations have become increasingly sophisticated and pervasive, posing significant threats to individuals, organizations, and governments worldwide. These malicious activities often leverage hidden online platforms to conduct illicit transactions, share stolen data, and coordinate attacks. One of the most notorious components of this underground ecosystem is darkmarket, a virtual marketplace where criminals buy and sell a wide range of illegal goods and services. The existence and expansion of darkmarket platforms highlight the importance of understanding their role in cybercrime networks and their impact on global security. Exploring these sites reveals the complex environment in which cybercriminals operate and underscores the necessity for robust cybersecurity measures.
Facilitation of Ransomware and Data Breaches
Darkmarkets serve as clandestine platforms where cybercriminals operate to facilitate a wide range of malicious activities, including the exchange of stolen data, illegal services, and weaponized hacking tools. These underground marketplaces are instrumental in enabling cybercriminal operations, often serving as hubs for organizing and executing cyber threats on a global scale. By providing anonymity and a secure environment, darkmarkets empower malicious actors to coordinate efforts with less fear of detection from law enforcement agencies.
The impact of these operations is profound, leading to significant financial and reputational damage for individuals and organizations alike. Cybercriminals frequently use darkmarkets to distribute ransomware, which encrypts victim data and demands payment for its release. These marketplaces also facilitate the sale and purchase of sensitive data breached from countless organizations, fueling identity theft, financial fraud, and corporate espionage. The ease of access and the availability of hacking tools within darkmarkets make it easier for even less sophisticated actors to launch complex cyberattacks, exacerbating the threat landscape.
One particularly concerning aspect is how darkmarkets contribute to the facilitation of ransomware and data breaches. Ransomware groups often collaborate within these platforms to purchase exploit kits, malware, or victim data, thereby streamlining their operations. This interconnected environment accelerates the spread of ransomware campaigns and enhances the sophistication of cyber attacks. As a result, organizations must remain vigilant, investing in robust cybersecurity measures to defend against these evolving threats that are fueled by the darkmarket ecosystem.
Impact on Cybersecurity and Online Crime
Darkmarkets serve as clandestine platforms where cybercriminal operations thrive, enabling the exchange of illegal goods and services with relative anonymity. These marketplaces play a significant role in facilitating various forms of online crime, ranging from drug trafficking to hacking tools and stolen data. The concealed nature of darkmarkets makes it challenging for authorities to detect and dismantle these networks, thereby perpetuating the cycle of cybercrime.
The impact of darkmarkets on cybersecurity is profound, as they often act as hubs for malicious activities. Cybercriminals utilize these platforms to buy and sell malware, ransomware, phishing kits, and other hacking resources that threaten both individuals and organizations. This proliferation of cyber threats increases the risk of data breaches, financial theft, and system disruptions, compromising the integrity of online infrastructure.
Furthermore, darkmarkets significantly contribute to the rise of online crime by lowering the barriers to entry for aspiring cybercriminals. They provide a marketplace environment where users can obtain sophisticated tools and stolen identities with ease, fueling a continuous cycle of crime. The global reach and anonymity offered by such platforms exacerbate the difficulty of enforcement and investigation efforts. Addressing the impact of darkmarkets requires collaborative efforts between law enforcement, cybersecurity experts, and policymakers to disrupt these illegal operations and strengthen digital defenses.
Role in Facilitating Cryptocurrency Crimes
Darkmarkets have emerged as clandestine digital marketplaces where cybercriminals orchestrate a wide range of illicit activities, significantly impacting global cybersecurity and financial ecosystems. These hidden platforms enable the exchange of illegal goods and services, often facilitating complex operations that evade legal oversight and traditional enforcement mechanisms.
Cybercriminal operations within darkmarkets involve various malicious activities, including drug trafficking, weapon sales, stolen data trading, and hacking tools. The anonymity provided by these platforms allows criminals to coordinate their efforts with minimal risk of detection, making them sophisticated hubs for cybercrime activities. These operations are often supported by advanced encryption and anonymity techniques that complicate efforts by authorities to trace and dismantle criminal networks.
One of the critical roles of darkmarkets is in facilitating cryptocurrency crimes. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin are commonly used within these platforms to conduct transactions due to their pseudonymous nature, which offers a higher degree of privacy compared to traditional banking methods. Darkmarkets serve as marketplaces where stolen financial information, hacking tools, and illicit services can be bought and sold using cryptocurrencies, thereby fueling a cycle of cybercrime that is difficult to disrupt.
The impact of these operations extends beyond financial loss; they undermine trust in online transactions and create significant security threats for individuals, businesses, and governments. The proliferation of darkmarkets complicates efforts to combat cybercrime, requiring enhanced cybersecurity measures, international cooperation, and continuous technological innovation to detect and dismantle these clandestine networks.
Understanding the structure and role of darkmarkets in cybercriminal operations is vital for developing effective strategies to combat their influence. As these platforms continue to evolve, stakeholders must stay vigilant and adapt to new tactics used by cybercriminals to ensure the safety and security of digital environments worldwide.
Notable Dark Marketplaces in 2024
In 2024, the landscape of dark marketplaces continues to evolve, with several notable platforms gaining prominence among users seeking a variety of illicit goods and services. These darkmarket platforms are often characterized by their anonymity features, resilience to takedowns, and expansive offerings. Understanding the most prominent dark marketplaces can help shed light on ongoing trends within this shadowy ecosystem and emphasize the importance of cybersecurity awareness and law enforcement efforts.
Leading Platforms and Their Features
Dark marketplaces, often referred to as darknets, are clandestine online platforms where illicit transactions take place, ranging from illegal drugs to stolen data. As the digital landscape evolves, several notable dark marketplaces have gained prominence in 2024, each with unique features designed to enhance security, anonymity, and user experience. These platforms operate in the shadows of the internet, attracting users seeking clandestine services and products.
One of the leading platforms in 2024 is recognized for its robust security protocols, including multi-layered encryption and decentralized hosting, which complicate law enforcement efforts. This marketplace prioritizes user anonymity by implementing advanced anonymization techniques, such as mandatory VPN use and secure payment methods. Its interface is user-friendly, featuring streamlined navigation and integrated escrow services to protect buyers and sellers alike.
Another notable darkmarket offers a comprehensive marketplace with a wide range of product categories, from digital goods to counterfeit documents. It boasts an active community of verified vendors and a reputation system that helps ensure transaction integrity. The platform emphasizes privacy, utilizing hidden web domains and regular security updates to prevent takedowns and malicious attacks.

The *darkmarket* epitomizes the ongoing innovation within these illicit platforms, showcasing features like anonymous messaging, multi-currency support, and rigorous vetting processes for vendors. Its resilience in the face of increasing surveillance highlights the adaptive nature of these marketplaces, constantly evolving to maintain anonymity and operational integrity.
Overall, the landscape of dark marketplaces in 2024 remains dynamic and complex, reflecting ongoing efforts to balance user needs with security challenges. While they operate outside legal boundaries, their technological sophistication and community-driven features make them significant points of interest in the realm of cybersecurity and digital privacy discussions.
Disappearances and Closure of Markets
Dark marketplaces, often known as darknet markets, have historically served as hubs for the exchange of a variety of goods and services outside the reach of conventional regulatory systems. As of 2024, several notable dark marketplaces have gained prominence due to their features, user base, or reputation, while others have faced sudden disappearances or closures, reflecting the ongoing volatility in this clandestine ecosystem.
One of the most recognized darkmarket platforms in recent years was XYZ Market, which attracted a large community of users thanks to its broad product range and relatively high-security measures. However, increased law enforcement efforts and internal security breaches have led to its eventual closure, highlighting the persistent risks faced by operators and users alike.
Another significant dark marketplace that made headlines in 2024 was Alpha Bazaar, known for its innovative escrow system and emphasis on privacy. Despite its popularity, Alpha Bazaar also experienced a mysterious disappearance, with users reporting that the platform abruptly went offline without warning. Such events underscore the fragile nature of these markets, often vulnerable to takedowns, scams, and betrayal by insiders.
Market closures often result from a combination of law enforcement crackdowns, server seizures, or the withdrawal of key administrators, which can cause sudden disruption for its user base. These disappearances pose challenges for individuals relying on these markets for their transactions, emphasizing the importance of understanding the risks involved in engaging with darkmarket platforms. The landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with new markets emerging while others vanish, driven by legal pressures, security concerns, and technological changes.
In 2024, the trend suggests that darkmarket operators are increasingly adopting sophisticated security measures and decentralization techniques to evade detection. Despite these efforts, the consistent pattern of notable market disappearances and closures indicates a persistent cat-and-mouse game with law enforcement agencies around the world. Users and vendors must exercise caution and remain aware of the volatile environment in which these platforms operate.
Influence of Raided or Ceased Markets on the Ecosystem
The landscape of dark marketplaces in 2024 continues to evolve, with several notable platforms shaping the underground economy. These marketplaces serve as hubs for a wide range of illicit activities, including drug trafficking, illegal weapons sales, and counterfeit goods. Despite increasing efforts by law enforcement agencies worldwide, new marketplaces frequently emerge to replace those that are raided or cease operations, reflecting the resilience and adaptability of these networks. The influence of raided or halted marketplaces significantly impacts the ecosystem, often disrupting supply chains temporarily while also driving users toward more secure or clandestine platforms. Such interventions can lead to the fragmentation of communities and the development of more sophisticated security measures in subsequent markets. As a result, the dark market ecosystem remains dynamic, with communities continuously adapting their tactics to evade detection and enforcement actions. Overall, these shifts underscore the persistent challenges faced by authorities in combating illegal trade and highlight the importance of understanding how these marketplaces evolve and influence each other over time.
Analytical Insights and Future Outlook
Analytical insights into the darkmarket landscape reveal a complex and ever-evolving environment driven by technological advancements and shifting security measures. Understanding the current trends and future prospects is essential for stakeholders aiming to address the challenges and opportunities within this clandestine marketplace. As the darkmarket continues to adapt, insights from recent reports highlight emerging patterns and potential developments that could influence both legal and security frameworks. For a deeper examination of the operational methods and threat intelligence, exploring various sources can provide valuable perspective, including platforms like darkmarket.
Monitoring Trends and Emerging Threats
Analytical insights into the darkmarket landscape reveal complex dynamics driven by technological advancements and shifting law enforcement strategies. Monitoring trends in this clandestine environment is essential for understanding how illicit activities evolve and adapt. The darkmarket ecosystem, characterized by its anonymity and encrypted communication channels, continuously witnesses new types of threats, such as sophisticated fraud schemes, counterfeit goods, and cybercriminal operations. As awareness grows, so does the need for innovative detection and prevention methods that can keep pace with the swiftly changing tactics employed by malicious actors.
Future outlooks suggest that the darkmarket will likely become more resilient through the adoption of emerging technologies such as blockchain, decentralization tools, and enhanced encryption techniques. These innovations can make tracking and dismantling illegal platforms increasingly difficult, necessitating a proactive and adaptive approach from security professionals and law enforcement. Continuous analysis of emerging threats, coupled with the development of advanced monitoring tools, will be vital for staying ahead in this ongoing battle. Effective intelligence gathering and collaboration among international agencies will also play a crucial role in combating activities within the darkmarket sphere, ensuring more robust defenses against evolving cyber threats.
Implications for Cybersecurity Professionals
As the landscape of digital commerce evolves, darkmarkets have become a prominent component of the cybercrime ecosystem, facilitating the anonymous exchange of illicit goods and services. Analytical insights into darkmarkets reveal significant trends, including the increasing sophistication of marketplaces, the consolidation of vendors, and the expansion of criminal offerings beyond traditional illegal drugs to include cyber weapons, stolen data, and counterfeit documents. These developments underscore the critical need for cybersecurity professionals to understand the operational mechanisms and threat vectors associated with these hidden hubs. Future outlooks suggest that darkmarkets will continue to adapt rapidly, leveraging emerging technologies such as cryptocurrencies and anonymization tools to evade law enforcement efforts. This dynamic environment demands that cybersecurity teams develop advanced monitoring capabilities, threat intelligence analyses, and proactive defense strategies to mitigate the risks posed by darkmarkets. The implications for cybersecurity professionals are profound, requiring ongoing education, collaboration across agencies, and investment in innovative detection tools to stay ahead of malicious actors operating within these concealed digital marketplaces. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of darkmarket activities is essential for safeguarding digital infrastructure and protecting organizations from a growing array of cyber threats.