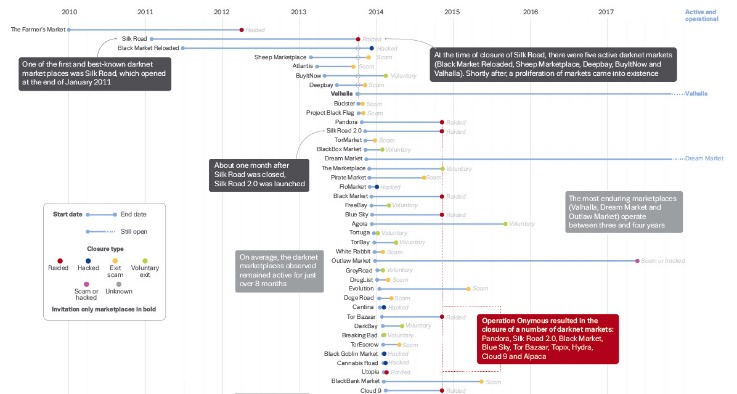
Overview of Darknet Markets
The darknet market is a hidden segment of the internet that operates on overlay networks, often accessed through specialized software like Tor. These markets facilitate anonymous transactions primarily involving illegal goods and services, creating a complex and often controversial landscape. As a virtual marketplace, they pose significant challenges for law enforcement and raise concerns about security, privacy, and illegal activity. Understanding how darknet markets function and their impact is essential for grasping the broader implications of online anonymity and illicit commerce. For more insights, explore a prominent darknet market example that highlights their operational intricacies.
Definition and Characteristics of Darknet Markets
Darknet markets are online platforms that operate within the dark web, providing a space for the buying and selling of various goods and services, often outside the scope of traditional legal and regulatory frameworks. These markets are accessed through specialized browsers that ensure user anonymity and privacy, making them attractive for activities that require confidentiality. Typically, participants in these markets use encrypted currencies, such as cryptocurrencies, to facilitate transactions, further enhancing their secrecy.
The defining characteristics of darknet markets include their hidden nature, reliance on anonymous communication methods, and the use of encrypted digital currencies. These platforms are usually hosted on the dark web, a part of the internet not indexed by standard search engines, and require specific software to access. They often feature hidden marketplaces with listings that can shift or change to avoid detection and shutdown by authorities. The combination of anonymity, encrypted transactions, and clandestine operations makes darknet markets distinct from regular online marketplaces, creating a unique ecosystem for illicit trade.
Role within the Darknet Ecosystem
The darknet market is a segment of the broader dark web where users can buy and sell a wide range of goods and services in anonymous environments. These markets operate using specialized encryption technologies and anonymity tools that protect the identity and location of both buyers and sellers. Typically accessed through browsers such as Tor, these marketplaces have become known for facilitating not only legal transactions but also illicit activities, including the sale of drugs, counterfeit documents, and stolen data.
Within the darknet ecosystem, these markets serve as critical hubs that connect vendors with customers seeking anonymity and privacy. They often feature user-friendly interfaces, secure payment methods—frequently using cryptocurrencies—and extensive moderation to maintain trust. The role of these markets extends beyond simple commerce, as they also influence the dynamics of cybercrime by enabling the distribution of illegal goods and services on a large scale. Their existence underscores the complex relationship between privacy technologies and criminal enterprises, highlighting ongoing challenges faced by law enforcement agencies worldwide.
Common Features Similar to Legitimate E-Commerce
Darknet markets are online platforms that operate on encrypted networks, allowing users to buy and sell a variety of goods and services. Despite their association with illegal activities, these markets often mimic the structure and features of legitimate e-commerce websites to facilitate transactions and attract users.
Many darknet markets share common features with traditional online stores. These include user-friendly interfaces, product listings with detailed descriptions and images, and secure payment systems. Typically, transactions are conducted using digital currencies to ensure anonymity and reduce the traceability of funds. Sellers often maintain feedback ratings and reviews, similar to legitimate e-commerce platforms, to build trust with buyers.
Another similarity is the use of escrow services, which hold funds until the buyer confirms satisfactory receipt of goods, reducing the risk of fraud. Darknet markets also have search functions, categorization of products, and customer support options, mirroring the functionalities users expect from mainstream online shopping sites. These features are designed to enhance user experience and streamline the buying and selling process.
- The dark web is an anonymized overlay of the internet accessible through networks such as Tor (“The Onion Router”), I2P and Riffle that utilize layered encryption to obscure the identities and locations of users.
- The results further support the recent efforts of law enforcement agencies to focus on individual sellers43,44,45, as well as, more recently, also buyers46,47.
- The new AlphaBay was filled with several new policies such as strict restrictions on selling Covid-19 vaccines, fentanyl, firearms, etc.
- Learn how darknet markets function and the challenges they present to cybersecurity, shedding light on the hidden side of the internet.
- She is a financial therapist and transformational coach, with a special interest in helping women learn how to invest.
However, despite these similarities, darknet markets operate in the shadows, often facilitating illicit activities that can pose significant legal and security risks. Understanding their common features helps users identify and navigate these platforms, but exercising caution and awareness of the legal implications is crucial when engaging with such markets.
Technical Infrastructure of Darknet Markets
The technical infrastructure of darknet markets plays a crucial role in maintaining their operation and ensuring user anonymity. These underground marketplaces rely on a complex network of secure servers, encrypted communications, and decentralized hosting to prevent detection and shutdown efforts. Sophisticated technologies such as Tor (The Onion Router) enable users to access these markets discreetly while protecting their identities. Additionally, many darknet markets utilize cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to facilitate transactions, further enhancing privacy and security. Understanding the underlying infrastructure is essential for comprehending how these illicit platforms function and persist in the digital landscape. For an example of a darknet market’s technical setup, visit this darknet market.
Use of Tor and Hidden Services
The technical infrastructure of darknet markets relies heavily on privacy-focused technologies that enable secure and anonymous transactions. Central to this infrastructure is the use of The Onion Router, commonly known as Tor, which provides a layered encryption system to conceal users’ identities and locations. By routing internet traffic through a network of volunteer-operated servers, Tor ensures that both buyers and sellers can operate with a high degree of anonymity, making it difficult for outside parties to trace activities back to individuals.
Darknet markets often operate as hidden services within the Tor network, accessible exclusively via the Tor browser. These hidden services utilize .onion domains, which are not accessible through standard web browsers, ensuring that the sites remain concealed from general internet searches. The use of onion services allows darknet markets to maintain operational security while facilitating the exchange of goods and services in an encrypted environment.
Security measures extend beyond just the use of Tor. Many darknet markets implement additional layers of encryption for communications and transactions, often involving cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, which offer pseudonymity instead of full anonymity. The infrastructure is designed to mitigate risks such as law enforcement intrusion and cyber attacks, creating a resilient environment for commerce that thrives under the cover of anonymity provided by Tor and its hidden services.
Overall, the technical backbone of such markets is predicated on advanced privacy-preserving technologies and decentralized networks, which collectively foster an environment where transaction confidentiality and user anonymity are prioritized. This infrastructure enables the persistent operation of darknet markets despite ongoing efforts by authorities to shut them down.
Cryptocurrency Transactions and Anonymity
The technical infrastructure of darknet markets is designed to facilitate anonymous and secure transactions within a concealed online environment. These markets often utilize specialized software that operates over the Tor network, ensuring user anonymity by encrypting communications and masking IP addresses. The underlying architecture typically relies on decentralized or distributed systems to prevent single points of failure, making it resilient against takedown attempts. This infrastructure supports a variety of features such as escrow services, encrypted messaging, and anonymous payment methods, all critical for maintaining user privacy and trust.
Cryptocurrency transactions play a central role in the operation of these markets, providing a degree of pseudonymity that traditional banking systems cannot offer. Most transactions on darknet markets are conducted using digital currencies like Bitcoin, which, despite their transparent public ledger, can be anonymized further through techniques such as coin mixing and tumbling services. These processes obscure transaction trails, making it difficult for authorities to trace the movement of funds and link them to specific individuals. The integration of cryptocurrency into the market infrastructure also allows for faster and borderless transactions, which are essential for the rapid and global nature of the illicit trade economy.
Maintaining anonymity is a priority for participants in darknet markets, which is achieved through a combination of technical measures and best practices. Users are encouraged to employ secure communication channels, avoid sharing identifiable information, and regularly update their software to protect against vulnerabilities. Market operators often implement advanced security protocols to safeguard user data and prevent attacks. The combination of robust technical infrastructure, cryptocurrency-based payments, and strict adherence to anonymity practices makes darknet markets a complex and resilient ecosystem, posing ongoing challenges for law enforcement and regulatory efforts.
Encryption and Security Features
The technical infrastructure of darknet markets is designed to ensure anonymity, security, and resilience against detection and takedown efforts. These markets typically operate on specialized networks that leverage layered encryption and decentralized architectures to protect users and vendors. Security features such as onion routing protocols are employed to anonymize communication, making it difficult for outsiders to trace transactions or identify participants. Cryptographic techniques are integral, securing data exchanges and transactions from potential interception or tampering. Many darknet markets incorporate multi-layer encryption for messaging, payment processing, and user authentication to enhance privacy and safeguard sensitive information. Additionally, these platforms often utilize decentralized hosting solutions or mirror sites to maintain availability even if primary nodes are compromised. Overall, the combination of advanced encryption, secure communication channels, and resilient infrastructure forms the backbone of the darknet market ecosystem, enabling it to operate in the shadows while attempting to minimize vulnerabilities associated with digital commerce.
Hosting and Accessibility of Dark Markets
The technical infrastructure of darknets plays a crucial role in enabling the operation and accessibility of darknet markets. These markets rely heavily on specialized hosting solutions, anonymization protocols, and secure communication channels to ensure user privacy and maintain their hidden status. Typically, darknet marketplaces are hosted on the Tor network, which provides an encrypted environment that shields both the server location and user identities from surveillance and tracing efforts. This hosting approach allows operators to establish stable and resilient platforms despite ongoing law enforcement efforts.
Darknet markets utilize a combination of robust encryption, decentralized hosting, and mirror sites to remain accessible even if primary servers are taken down. Multi-layered security measures are implemented, including digital signatures, encrypted messaging systems, and secure payment methods, often involving cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Monero to facilitate anonymous transactions. Accessibility is further enhanced through the use of onion services, which hide the server’s IP address, making it difficult for authorities to locate and shut down these platforms.
The underlying infrastructure also involves the creation of resilient network architectures that can withstand Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks and other disruptions. Market operators frequently employ infrastructure redundancy, distributed hosting, and mirror sites to ensure uninterrupted access for users. These technical strategies collectively sustain the operational integrity and anonymity of dark markets, allowing them to function clandestinely in the complex landscape of online illicit activities. The combination of secure hosting, advanced encryption, and persistent accessibility mechanisms forms the backbone of the darknet marketplace ecosystem.
Types of Illicit Goods and Services Offered
The darknet market is a hidden segment of the internet where a wide range of illicit goods and services are exchanged. These underground platforms facilitate the sale and distribution of illegal items, often operating anonymously to evade law enforcement. Such marketplaces deal with a variety of prohibited products, including drugs, counterfeit currency, stolen data, and weapons. Understanding the types of illicit goods and services offered on these markets is crucial for grasping their impact on global security and the challenges faced by authorities. Visitors can explore different darknet markets to learn more about the scope of illegal activities taking place behind the anonymity of the dark web.
Stolen Data and Credentials
Darknet markets are online platforms that facilitate the exchange of a variety of illicit goods and services, often operating anonymously through encrypted networks. These markets provide users with access to items and services that are typically illegal, creating a thriving underground economy.
One of the primary categories of illicit goods available on darknet markets includes various types of illegal substances. These often range from narcotics and controlled pharmaceuticals to synthetic drugs, making them easily accessible to a broad audience. Additionally, counterfeit items such as fake IDs, forged documents, and imitation luxury goods are frequently sold.
Another significant aspect of darknet markets is the offering of stolen data and credentials. Cybercriminals utilize these platforms to trade sensitive information including stolen credit card details, personal identification data, login credentials for various online accounts, and hacking tools. These stolen data sets are often used to commit fraud, identity theft, or unauthorized access to secure systems.
Illicit services are also commonly available within these markets, including hacking, malware development, and illegal hacking services. Users can hire cybercriminals to conduct specific malicious activities, such as data breaches or Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
In summary, darknet markets serve as hubs for a variety of illegal activities, offering:
- Illegal drugs and pharmaceuticals
- Counterfeit and fake items
- Stolen personal and financial data
- Hacking tools and services
- Other illicit services and goods
Drugs, Weapons, and Counterfeit Currency
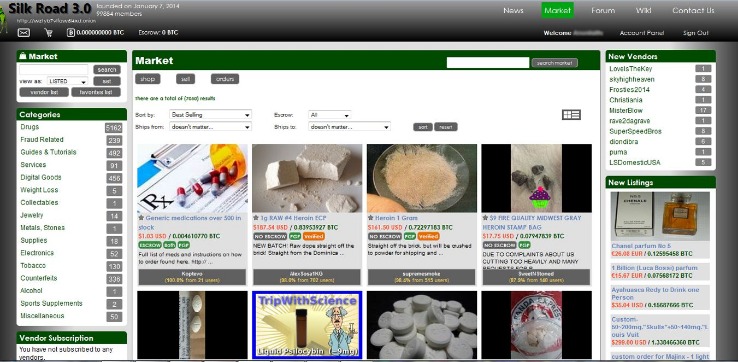
Darknet markets are known for facilitating the exchange of various illicit goods and services, often operating outside legal boundaries. Among the most common offerings are drugs, where a wide range of substances, from recreational to harder narcotics, are bought and sold with relative anonymity. These platforms enable users to access substances without traditional regulations or oversight, raising significant concerns about public health and safety. Additionally, weapons are another category of illicit items available through darknet markets, including firearms, ammunition, and sometimes even explosives, which pose serious threats to security and law enforcement efforts.
Counterfeit currency and forged documents are also frequently exchanged within these hidden online environments. These counterfeit items can be used for financial crimes, enabling individuals to launder money or carry out illegal transactions with fake bills, further complicating investigations and enforcement actions. The nature of such illicit goods and services underscores the ongoing challenges faced by authorities worldwide in combating illegal activities on the darknet, a space where anonymity is often prioritized to evade detection. The presence of these dangerous commodities highlights the importance of continuous efforts to monitor and disrupt these illicit networks to protect society.
Hacking Tools and Malware Services
The darknet market is a hidden segment of the internet where illegal goods and services are commonly bought and sold, often operating beyond the reach of traditional law enforcement. Among the most prevalent offerings are illicit goods such as illegal drugs, counterfeit currency, and stolen data. These markets facilitate transactions in a clandestine environment, often utilizing cryptocurrencies to maintain user anonymity. Another significant category involves the sale of hacking tools and malware services, which enable cybercriminals to compromise systems, spread malicious software, or conduct targeted cyberattacks. These hacking tools range from exploit kits to remote access Trojans, all designed to facilitate unauthorized access to individuals or organizations. Malware services include the creation and distribution of viruses, ransomware, and spyware, which can be employed for extortion, data theft, or disrupting operations. The dark web’s anonymous nature makes it an attractive platform for those seeking malicious tools and illicit services, perpetuating threats to individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Efforts to combat these activities are ongoing, but the dark web remains a challenging environment for law enforcement due to its encryption and anonymity features, especially within darknet markets that frequently host such illegal transactions.
Services for Cybercrime and DDoS Attacks
Darknet markets are known for facilitating the exchange of various illicit goods and services beyond the reach of traditional regulatory systems. These platforms serve as hubs where illegal activities such as the sale of narcotics, stolen data, counterfeit currencies, and weapons are conducted with a level of anonymity that complicates law enforcement efforts. The anonymity offered by the darknet allows these markets to flourish despite ongoing efforts to shut them down and disrupt their operations.
One of the key areas within these markets involves the offering of illicit goods, including drugs, firearms, and endangered species. These goods are often procured and traded through encrypted channels, making detection and intervention challenging. Besides physical illegal items, these markets also host a variety of services that cater to cybercriminal activities.
Among the most prevalent offerings are services for cybercrime, such as hacking tools, malware, and phishing kits. These services enable malicious actors to compromise systems, steal sensitive information, or disrupt online services. Additionally, the darknet plays a significant role in facilitating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which are used to overwhelm targeted websites with traffic, rendering them inaccessible. The sale of such services often includes technical support, allowing less experienced malicious actors to execute cyberattacks with relative ease.
The extensive range of illicit goods and cybercrime services available in darknet markets underscores the ongoing threats faced by businesses, governments, and individuals. Combating these activities requires coordinated international efforts and advanced cybersecurity measures to monitor and disrupt illegal online operations effectively.
Operational Aspects of Dark Markets
Darknet markets operate as hidden online marketplaces that facilitate the exchange of goods and services beyond the reach of conventional law enforcement and regulatory oversight. These markets rely heavily on encrypted communication channels and anonymizing technologies to protect the identities of both buyers and sellers. A key aspect of these platforms involves complex operational structures, including secure transaction processes, escrow services, and strict user verification mechanisms. Understanding the operational aspects of a *darknet market* is essential for comprehending how illicit trade persists in these hidden environments. For instance, some markets utilize specialized tools and websites to ensure privacy and security, such as the marketplace found at Darknet Market, ensuring that participants can conduct transactions with minimized risk of detection.
Escrow and Trust Mechanisms
Darknet markets, often referred to as dark markets, operate within the hidden layers of the internet, providing a platform for anonymous transactions. These markets rely heavily on specialized operational mechanisms to ensure the integrity and security of transactions despite the illicit nature of many of their offerings. Central to their functioning are escrow services and trust mechanisms that help mitigate risks for buyers and sellers participating in these clandestine exchanges.
One of the key operational aspects of dark markets is the implementation of escrow services. These services act as neutral third parties that hold funds during transactions until the buyer confirms satisfactory receipt of goods or services. If the buyer is pleased, the escrow releases the funds to the seller; if there are issues, a dispute resolution process is initiated. This system reduces the likelihood of fraud and increases confidence among market participants.
Trust mechanisms in dark markets often include reputation systems, feedback ratings, and escrow usage. These systems incentivize honest behavior by allowing users to rate each other based on their transaction experience. A robust reputation system helps new users identify reliable vendors, which is critical in environments where anonymity can complicate trust. Many markets also incorporate multisignature escrow transactions, adding an additional layer of security by requiring multiple approvals before funds are released.
Operational aspects also extend to dispute resolution procedures, which are vital for maintaining order and trust. When conflicts arise, market administrators or automated systems intervene to assess evidence and resolve disputes fairly. Regular monitoring, security protocols, and enforced escrow use contribute to the overall stability and security of dark marketplaces, making them operationally complex but functional.
- Implementation of escrow services to hold funds securely until transaction completion.
- Use of reputation and feedback systems to foster trust among anonymous users.
- Deployment of multisignature transactions for added security.
- Dispute resolution processes to handle transactional conflicts effectively.
- Security measures to prevent fraud and maintain marketplace integrity.
Market Lifecycle and Evasion Tactics
Darknet markets, often referred to as dark markets, are clandestine online platforms that facilitate the exchange of goods and services outside the scope of conventional regulation and oversight. These markets operate within the dark web, using encrypted networks to maintain user anonymity and security. Understanding the operational aspects of dark markets involves examining their lifecycle, from launch and growth to eventual decline, as well as the evasion tactics employed to avoid detection and shutdown by authorities.
The lifecycle of a darknet market typically begins with a discreet launch by administrators seeking to establish a reliable platform for vendors and buyers. During the initial phase, the market’s focus is on attracting users through reputation mechanisms, escrow services, and secure payment systems, often utilizing cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to obscure transaction origins. As it gains popularity, the market expands its vendor base and product offerings, striving to build trust and a steady user flow. Over time, some markets achieve a stable position, becoming prominent players within the ecosystem.
However, the operational sustainability of these platforms is challenged by law enforcement efforts and internal security threats. To evade detection, operators frequently change domain names, employ decentralized hosting solutions, and deploy sophisticated encryption and anonymization techniques. Vendors and buyers also adopt encryption tools and privacy-focused communications to avoid interception. These evasion tactics are continually refined to stay ahead of authorities attempting to infiltrate or shut down these markets.
The evasion strategies extend to the use of layered security measures, including multi-signature escrow systems, role-based access controls, and frequent updates to software and infrastructure. Such measures complicate efforts to identify and dismantle darknet markets. Despite these precautions, law enforcement agencies worldwide undertake coordinated operations aiming to disrupt these platforms, often resulting in temporary closures, arrests, and the seizure of illicitly gained assets.
In conclusion, understanding the operational aspects of darknet markets reveals a complex interplay between market dynamics and law enforcement countermeasures. These markets continually adapt their lifecycle stages and employ advanced evasion tactics to sustain their clandestine operations. Recognizing these patterns is vital for developing effective strategies to combat illegal activities associated with them while respecting the broader implications for privacy and digital freedoms.
Reputation Systems and User Reviews
The operational aspects of dark markets involve complex structures and systems that facilitate the anonymous exchange of goods and services. These marketplaces operate primarily on the darknet, leveraging specialized technology to maintain user privacy and security. Key components include encrypted communication channels, anonymous payment methods, and strict access controls to prevent unauthorized intrusion. The anonymity provided by these systems aims to protect both buyers and sellers from law enforcement and other threats, although it also presents significant challenges related to trust and safety.
Reputation systems play a critical role in maintaining order and accountability within dark markets. Since users often operate anonymously, reputation scores and feedback mechanisms serve as proxies for trustworthiness and reliability. Buyers typically leave reviews after transactions, which are then visible to the community, helping others make informed decisions. However, the effectiveness of these systems depends on their integrity; malicious actors may attempt to manipulate reviews or create fake accounts to artificially boost reputations, leading to issues of credibility and potential fraud.
User reviews are integral to the functioning of dark markets, providing transparency and community-driven validation of vendors and products. These reviews often include detailed descriptions of transaction experiences, product quality, and customer service. While they help foster a semi-structured marketplace environment, challenges arise due to potential fake reviews, retaliatory feedback, or coordinated manipulation. Market operators continuously develop and refine verification processes to mitigate these risks, ensuring that feedback remains a valuable and accurate resource for participants.
Overall, the operational dynamics of dark markets are shaped by sophisticated technological solutions and community-driven trust mechanisms. Ensuring the integrity of reputation systems and reviews remains a significant focus, as maintaining trust is essential for the continued function of these clandestine economies.
Impacts and Risks Associated with Darknet Markets
Darknet markets are online platforms that facilitate the exchange of goods and services, often operating beyond the reach of traditional regulatory frameworks. While they provide anonymity for users, these markets also pose significant risks and challenges. The illicit nature of many transactions on darknet markets can lead to financial fraud, exposure to illegal products, and involvement in criminal activities. Furthermore, accessing these markets may inadvertently expose users to cybersecurity threats and legal consequences. Understanding the impacts and risks associated with darknet markets is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their negative effects and enhance online safety. For more information on secure online practices, visit our comprehensive guide on darknet market safety and management.
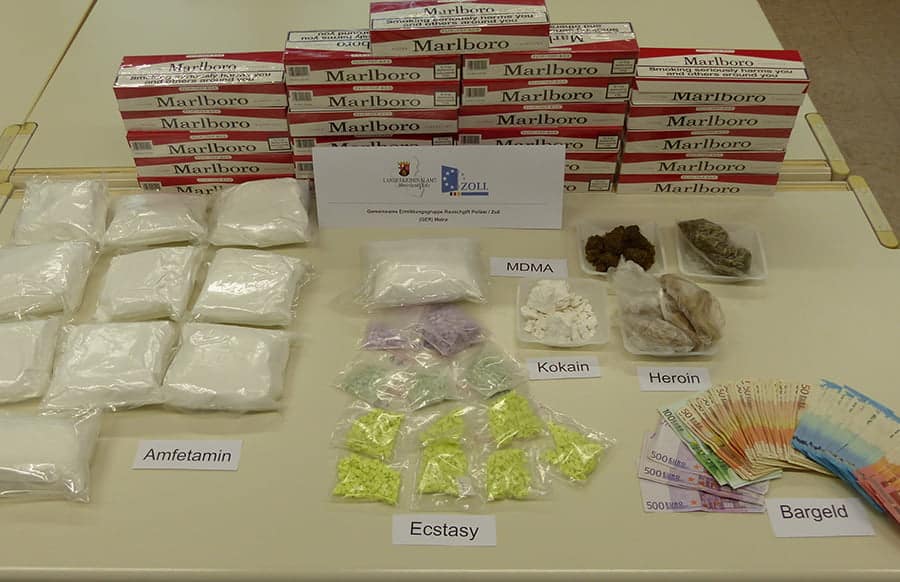

Facilitation of Cybercrime and Data Breaches
Darknet markets, hidden online platforms accessible via specialized networks, have become significant hubs for illicit activities, posing serious impacts and risks to global cybersecurity and public safety. These markets facilitate a wide range of illegal transactions, including the sale of drugs, stolen data, and counterfeit goods, which contribute to the proliferation of cybercrime worldwide.
The facilitation of cybercrime through darknet markets significantly increases the likelihood of data breaches. Criminal actors often utilize these platforms to distribute stolen personal and financial information, making individuals and organizations vulnerable to identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities. The anonymous nature of these markets complicates law enforcement efforts, enabling cybercriminals to operate with minimal risk of detection or apprehension.
Furthermore, the dark web’s environment fosters the exchange of hacking tools, malware, and exploits, which can be employed to infiltrate networks, compromise systems, and cause extensive damage. The influx of such malicious resources escalates the sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks, undermining digital security infrastructures worldwide.
While **darknet markets** provide a platform for illicit exchanges, they also pose broader societal risks by enabling criminal enterprises to thrive and expand. The increased availability of illegal goods and services perpetuates criminal networks, fuels violence, and undermines trust in digital transactions. Addressing these issues requires a coordinated effort among cybersecurity professionals, law enforcement agencies, and policymakers to mitigate the impacts and risks associated with darknet markets and their role in facilitating cybercrime and data breaches.
Nation-State Use and Cyber Warfare
Darknet markets are online platforms that facilitate the anonymous exchange of goods and services, often operating outside the reach of traditional law enforcement. While they provide a means for privacy and free trade, they also pose significant risks to global security and stability. The covert nature of these markets makes them attractive for illicit activities, including drug trafficking, weapons sales, and cybercriminal operations, which can have far-reaching consequences for societies and economies.
One major impact of darknet markets is their facilitation of cybercrime, which includes hacking services, stolen data, and malware sales. Such activities can be exploited by malicious entities, including nation-states, to conduct espionage, sabotage, or large-scale cyber attacks. The use of darknet channels by nation-states significantly elevates the threat level, as it allows covert operations that can undermine governments, disrupt critical infrastructure, or influence foreign elections. These activities contribute to heightened geopolitical tensions and domestic vulnerabilities.
The risks associated with darknet markets extend into the realm of cyber warfare, where state and non-state actors leverage these platforms for strategic advantages. Cyber warfare can involve targeted attacks on financial institutions, denial-of-service assaults, and the dissemination of disinformation campaigns. These operations can destabilize economies, weaken national security, and challenge international norms. Additionally, the anonymous environment of darknet markets complicates efforts to track and prosecute perpetrators, making it easier for malicious entities to operate with impunity.
Furthermore, the proliferation of darknet markets raises concerns over the proliferation of illegal weapons and dangerous substances, which can escalate violence and undermine public safety. The ease of access and the pseudonymous nature of transactions create an environment where dangerous items can circulate widely without proper oversight. This not only intensifies criminal activities but also complicates efforts by law enforcement agencies worldwide to combat these threats effectively.
In sum, darknet markets represent a complex challenge with profound impacts that extend beyond individual criminals to include nation-states and their strategic interests. Addressing these risks requires coordinated international efforts, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and policies aimed at disrupting illicit networks while preserving legitimate privacy rights.
Threats to Businesses and Personal Security
The darknet market represents a hidden sector of the internet where illegal goods and services are bought and sold with relative anonymity. While it offers a platform for covert transactions, it also poses significant impacts and risks to both businesses and personal security. Engaging with or unknowingly being associated with these markets can lead to severe legal and financial consequences.
One of the primary impacts of darknet markets is the facilitation of illegal activities such as drug trafficking, weapons sales, counterfeit currency, and stolen data exchanges. These activities contribute to an increase in organized crime and undermine lawful commercial operations. Businesses that inadvertently interact with these markets risk being exploited or targeted by cybercriminals, which can result in data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Personal security is also at high risk, as individuals involved in darknet markets may be subject to scams, identity theft, or blackmail. Law enforcement agencies continually work to dismantle these markets, but users and vendors often operate under high levels of anonymity, making them vulnerable. Moreover, the usage of cryptocurrencies for transactions, while offering some privacy benefits, complicates law enforcement efforts and facilitates illicit dealings.
For businesses, the presence of darknet markets can escalate threats from cyberattacks, including hacking, phishing, and malware targeting their infrastructure. Such threats not only compromise sensitive information but can also disrupt operations and lead to fiscal losses. Individuals, especially those dealing with sensitive personal data, face the risk of exposure and financial fraud.
Overall, the risks linked to darknet markets underscore the importance of strong cybersecurity measures, vigilant monitoring, and adherence to legal standards. Preventative strategies and awareness are crucial to safeguarding both enterprise integrity and personal security from the negative impacts associated with these clandestine online platforms.
Challenges for Law Enforcement and Cybersecurity Professionals
The emergence of darknet markets has significantly transformed the landscape of illegal activities on the internet, presenting numerous impacts and risks for both society and individual users. These hidden platforms facilitate the anonymous exchange of illegal goods and services, including drugs, weapons, stolen data, and counterfeit items, often operating beyond the reach of traditional law enforcement channels. As a result, they contribute to increased criminal activity and pose challenges to public safety and security.
One of the primary concerns associated with darknet markets is the proliferation of illicit trade, which can fund violent organizations, terrorism, and other forms of organized crime. The anonymity provided by the darknet complicates efforts to trace transactions and identify perpetrators, making it difficult for authorities to intervene effectively. Moreover, the rise of these markets amplifies risks related to consumer safety, as buyers may inadvertently purchase counterfeit or dangerous products, with little recourse for resolution.
For law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity professionals, the darkweb represents a complex challenge requiring advanced techniques and persistent efforts. Investigating activities within darknet markets involves overcoming technical barriers such as encryption, IP masking, and decentralized networks. These hurdles demand significant resources, specialized skills, and a coordinated approach across jurisdictions. Additionally, the rapid evolution of darknet platforms and the use of cryptocurrencies for transactions further complicate efforts to monitor and disrupt illegal operations.
Cybersecurity professionals must also contend with the threat of cyberattacks, data breaches, and malware linked to darknet activities. Criminals leveraging this hidden network often employ sophisticated methods to evade detection, making it crucial for cybersecurity strategies to stay ahead of emerging threats. The risks extend beyond criminal enterprises, as cybersecurity vulnerabilities arising from darknet-related activities can impact critical infrastructure, financial systems, and private data, underscoring the importance of robust security measures.
Overall, the impacts and risks associated with darknet markets pose significant challenges that require a multifaceted response from law enforcement, cybersecurity experts, policymakers, and the global community. Addressing these issues involves enhancing investigative techniques, developing better tools for online anonymity management, and fostering international cooperation to combat illegal activities effectively while safeguarding individual rights.
Countermeasures and Security Strategies
In the complex and often clandestine world of darknets, security strategies and countermeasures are essential to protect users and maintain operational integrity. Darknet markets, known for their anonymous transactions and hidden operations, face constant threats from law enforcement, cybercriminals, and internal breaches. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious activities. This article explores effective techniques for safeguarding digital assets, including encryption, access controls, and vigilant monitoring, to ensure the safety and stability of darknet market operations. For additional insights into security practices, you can explore related darknet market resources.
Monitoring and Infiltrating Dark Markets
Darknet markets are clandestine online platforms that facilitate the exchange of illicit goods and services, often operating beyond the reach of conventional regulatory frameworks. Due to their covert nature, law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals employ a variety of countermeasures and security strategies to monitor, infiltrate, and dismantle these hidden networks. Accurate intelligence gathering and technological innovation are critical for understanding the structure and operations of these markets.
Effective countermeasures typically involve advanced digital surveillance tools, including traffic analysis, malware infiltration, and undercover operations to trace illicit transactions. Virtual private networks (VPNs), encryption techniques, and anonymizing services like Tor are both tools used by operators and challenges for investigators, necessitating sophisticated methods to de-anonymize users and identify key players. Regular intelligence sharing among international agencies enhances coordinated efforts to disrupt darknet marketplaces.
Security strategies include proactive monitoring of emerging forums and marketplaces, analyzing patterns of activity, and leveraging artificial intelligence to detect illegal transactions or precursor behaviors. Cybersecurity teams also focus on identifying vulnerabilities within darknet infrastructure, whether through malware analysis or examining transaction data, to predict and prevent illicit activity.
Monitoring these markets involves continuous observation of marketplace activity, transaction flows, and user behavior to gather actionable intelligence. Techniques such as blockchain analysis aid in tracking crypto transactions linked to illegal trade, while social network analysis helps identify the network of operators behind various marketplaces. Such comprehensive monitoring aids law enforcement officials in creating a detailed picture of the darknet ecosystem.
Infiltration efforts require a careful balance of technical expertise and operational security. Law enforcement agents often create undercover profiles or fake marketplaces to gain trust within these communities, enabling them to gather intelligence and identify major vendors and facilitators. This approach aids in leading targeted takedown operations, ultimately disrupting the supply chains and financial flows sustaining these illegal markets.
Threat Intelligence and Advanced Detection Tools
Effective countermeasures and security strategies are essential for safeguarding digital infrastructures from malicious activities associated with darknet markets. These illicit platforms pose significant threats by facilitating illegal transactions, distributing malicious software, and enabling cybercriminal operations. Implementing comprehensive threat intelligence allows organizations to stay informed about emerging risks and tactics used by cybercriminals operating within these hidden ecosystems. By continuously analyzing patterns, behaviors, and attack vectors, security teams can develop proactive defenses that mitigate potential damages.
Advanced detection tools play a crucial role in identifying suspicious activities and unauthorized access attempts linked to darknet market activities. Techniques such as machine learning algorithms, behavioral analytics, and traffic analysis can unearth anomalies indicative of cyber threats. Integrating these tools within security infrastructures enhances real-time monitoring capabilities and enables swift response to potential breaches. Furthermore, employing encryption and secure communication protocols inhibits unauthorized interception of sensitive information, thereby reinforcing digital defenses against cybercriminal exploits.
Given the covert nature of darknet markets, organizations must adopt layered security strategies encompassing cybersecurity best practices, continuous threat intelligence gathering, and state-of-the-art detection technologies. By fostering a proactive security posture, businesses can better anticipate, detect, and respond to challenges posed by illicit online activities, ultimately safeguarding their assets and maintaining trust in their digital environments.
International Collaboration and Legal Frameworks
Countermeasures and security strategies are essential in addressing the challenges posed by illicit activities within the darknet market. Law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity organizations implement a combination of technological tools, intelligence sharing, and proactive monitoring to identify and dismantle illegal networks. Advanced tracking techniques, such as digital forensics and metadata analysis, help uncover connections and trace transactions, while anonymization obfuscation methods are continually countered with innovative de-anonymization tools. Strengthening cybersecurity infrastructure and raising awareness among stakeholders also play pivotal roles in preventing cybercriminal activities associated with the darknet.
International collaboration is crucial in combating the complex and transnational nature of illegal operations on the darknet. Countries and international organizations work together through joint task forces, information exchange agreements, and coordinated operations to disrupt illicit markets. Shared intelligence allows for a more comprehensive understanding of criminal networks and enhances the ability to take timely action. Establishing common standards and protocols facilitates cross-border cooperation, ensuring a unified response to emerging threats. This collaborative effort helps dismantle global illegal marketplaces and reduces their impact on society.
Legal frameworks are fundamental in establishing the boundaries and authorities needed to pursue cybercriminals operating within the darknet. Many nations have enacted legislation that criminalizes activities like drug trafficking, weapons trade, and money laundering conducted through illegal online marketplaces. Effective legal measures also involve safeguarding privacy rights while enabling law enforcement to access necessary data during investigations. International treaties and conventions further harmonize legal procedures and obligations, promoting a consistent approach to prosecuting offenders and enforcing sanctions. Robust legal frameworks underpin the ongoing efforts to secure the digital environment and diminish the appeal of underground markets such as the darknet.
Employee Training and Preventive Measures for Organizations
Understanding and implementing effective countermeasures and security strategies are essential for organizations operating in environments where darknet markets may pose risks. These markets often facilitate illegal activities that can impact legitimate enterprises through cyber threats, data breaches, and financial fraud. To mitigate such risks, organizations should adopt a comprehensive approach encompassing technological safeguards, employee awareness, and proactive policies.
One of the foundational strategies involves deploying advanced security solutions such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and endpoint protections to monitor and block malicious activities. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited. Additionally, implementing multifactor authentication and robust access controls reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
Employee training is a critical component in strengthening an organization’s defenses. Regular educational programs should focus on recognizing phishing scams, avoiding suspicious links, and understanding the tactics used by cybercriminals involved in darknet markets. Well-informed employees are less likely to inadvertently facilitate security breaches or fall victim to social engineering attacks.
Preventive measures should include strict data handling procedures, timely software updates, and comprehensive incident response plans. These measures prepare the organization to respond swiftly and effectively in case of a security incident, minimizing potential damages. Monitoring network activity for unusual patterns and suspicious transactions can also alert organizations to potential threats early on.
In the context of the darknet market, organizations need to stay vigilant about emerging threats and evolving cybercriminal strategies. Collaboration with cybersecurity experts and participating in industry information-sharing initiatives can provide insights into current tactics and help develop targeted defenses. By maintaining a proactive security posture, organizations can better protect their assets and uphold the integrity of their operations in an increasingly complex digital landscape.