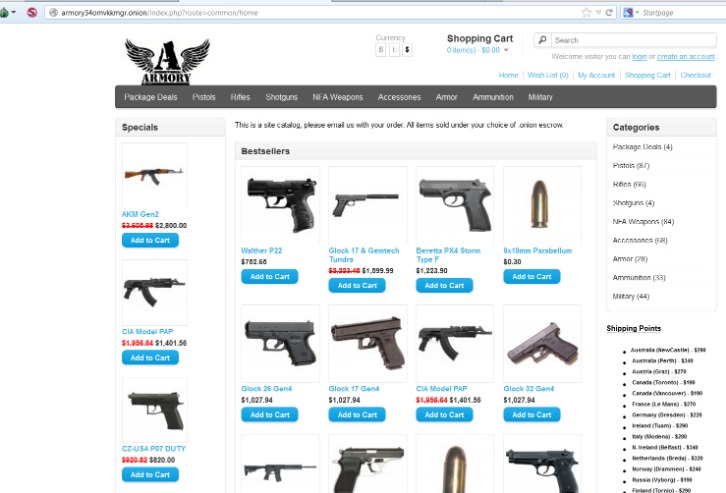
Overview of Dark Web Marketplaces
The dark web is a hidden part of the internet that requires special software and configurations to access. Among its many features are clandestine marketplaces that facilitate the exchange of goods and services outside the reach of traditional legal systems. These dark web marketplaces provide a platform for traders and buyers to operate anonymously, often dealing in both legal and illegal items. Understanding these marketplaces is crucial for maintaining cybersecurity and awareness about online privacy and risks. For those interested, there are various dark web marketplaces where users can explore different types of offerings, such as safe shopping options or specialized services.
Definition and Characteristics of Dark Web Markets
The dark web marketplaces are a segment of the internet that operates beyond the reach of traditional search engines and standard online browsing. These platforms are primarily accessed through specialized networks such as Tor, ensuring anonymity for both buyers and sellers. Dark web marketplaces serve as digital hubs where various goods and services, some legal but many illegal, are bought and sold covertly. They often feature encrypted communication, hidden identities, and secure payment methods to protect users’ privacy and maintain the illicit nature of transactions.
Characteristic features of dark web markets include their reliance on decentralized or peer-to-peer structures, making them resistant to shutdown efforts. They typically use cryptographic tokens or cryptocurrencies for transactions, which add an extra layer of anonymity. These marketplaces often operate with strict community rules, feedback systems, and escrow services to facilitate trust despite the clandestine environment. The nature of the products exchanged can range from legal items such as digital software to illegal commodities like drugs, weapons, or stolen data. Understanding these characteristics is essential for recognizing the vulnerabilities and risks associated with dark web marketplaces and their impact on cyber security and law enforcement efforts.
Infrastructure and Access Methods
The dark web is a hidden part of the internet that is not accessible through standard search engines and requires specialized software to access. Among its various components, dark web marketplaces are platforms where users can buy and sell a wide range of goods and services, often operating outside the boundaries of legal regulation. These marketplaces provide an anonymous environment, making them attractive for illicit transactions, but also pose significant challenges for law enforcement and cybersecurity efforts.
The infrastructure of dark web marketplaces relies heavily on peer-to-peer networks and encrypted communication protocols to ensure user anonymity and security. Most of these platforms are hosted on the Tor network, a popular anonymity-preserving network that directs internet traffic through a worldwide, volunteer overlay network to conceal users’ identities and locations. Many marketplaces incorporate complex multi-layered encryption and utilize cryptocurrency transactions, typically Bitcoin or other digital currencies, to facilitate anonymous payments.
Access to these marketplaces generally requires users to utilize specialized software like the Tor Browser, which allows them to browse anonymously without revealing their IP addresses or physical locations. Users often need to create accounts with pseudonymous identities, and marketplaces employ various security measures, including enforced escrow services, reputation systems, and hidden communication channels, to safeguard transactions and build trust. Despite these protections, navigating the dark web market environment comes with inherent risks, such as scams, law enforcement interventions, and exposure to illegal content.
Understanding the infrastructure and access methods of dark web marketplaces is crucial for cybersecurity professionals, law enforcement agencies, and policymakers who aim to combat criminal activities while respecting privacy rights. The landscape is constantly evolving, with marketplaces frequently changing domains, implementing new security measures, and adapting to legal actions to remain operational.
Types of Goods and Services Offered
Dark web marketplaces are online platforms that operate on the concealed areas of the internet, often utilizing anonymity tools to protect user identities. These marketplaces serve as digital hubs where a variety of goods and services are bought and sold outside the reach of traditional regulatory oversight. They are typically accessed through specialized networks that prioritize privacy and security, making them difficult for law enforcement to monitor and regulate.
These marketplaces facilitate a wide range of transactions, from legal to highly illegal activities. Commonly offered goods include illicit drugs, counterfeit currencies, stolen data, and unlicensed pharmaceuticals. They also host markets for weapons, hacking tools, and counterfeit documents. Additionally, some platforms provide services such as hacking, hacking-as-a-service, money laundering, and other criminal activities. The diverse offerings reflect both the demand for illegal products and services and the ability of *dark web marketplaces* to adapt quickly to emerging trends and law enforcement measures.
Understanding the types of goods and services offered on these platforms is crucial for grasping the scope of their impact. While many transactions are illegal, some marketplaces may also deal with legal items like rare collectibles or digital assets. However, the emphasis remains on illicit commerce, which poses significant challenges for authorities worldwide. Awareness of these marketplaces and their offerings is vital for cybersecurity professionals and legal authorities working to combat cybercrime and maintain online security.
History and Evolution of Dark Web Marketplaces
The history and evolution of dark web marketplaces reveal a fascinating journey from anonymous forums to complex online hubs for goods and services. Originally emerging in the early 2000s, these marketplaces provided users with a platform to buy and sell items clandestinely, often emphasizing privacy and anonymity. Over time, they evolved to incorporate sophisticated security measures, encryption technologies, and decentralized systems to mitigate risks and law enforcement interference. Today, dark web marketplaces serve various purposes, from illicit trades to privacy-focused transactions, reflecting both technological progress and shifting legal landscapes. For those interested in exploring these platforms, there are a number of established marketplaces that have maintained operations through innovative methods and resilient infrastructures. One such marketplace offers a wide array of services and goods in a secure environment, accessible through specialized browsers and network configurations, exemplifying the ongoing development and significance of this hidden digital economy. For more resources on dark web marketplaces, visit trusted platforms that facilitate secure access and information sharing in this realm.
Origins with Silk Road
The history and evolution of dark web marketplaces showcase a complex journey rooted in the desire for anonymous transactions and decentralized commerce. These marketplaces developed as a response to increasing concerns over privacy and government surveillance, providing a platform where users could buy and sell a wide range of goods without revealing their identities. The dark web, a part of the deep web accessible only through specialized software, became the foundation for these clandestine markets.
The emergence of dark web marketplaces can be traced back to the early 2010s, with the most notable being Silk Road. Launched in 2011 by Ross Ulbricht, Silk Road revolutionized online black markets by utilizing the Bitcoin blockchain for transactions, allowing for a higher level of anonymity. This marketplace primarily facilitated the sale of illegal drugs but also expanded to include other illicit goods and services. Silk Road’s success demonstrated the potential of decentralized marketplaces and inspired the development of numerous similar platforms.
Following Silk Road’s shutdown in 2013 by law enforcement agencies, many successors appeared, often trying to improve on the vulnerabilities of earlier versions. These platforms employed advanced security measures, layered encryption, and decentralized hosting to evade detection. Their evolution reflects an ongoing cat-and-mouse game between authorities and marketplace operators. Over time, dark web marketplaces diversified beyond illicit substances to encompass hacking tools, stolen data, counterfeit currencies, and other illegal commodities.
The development of dark web marketplaces signals the broader trend of digital underground economies that continuously adapt to technological innovations and law enforcement tactics. While these platforms facilitate illicit activities, they also raise complex issues surrounding privacy, security, and regulation in the digital age. As these marketplaces continue to evolve, understanding their history provides insights into their resilience and the challenges faced in combating illegal online trading networks.
Major Marketplaces and their Lifespans
The history and evolution of dark web marketplaces reflect a complex landscape driven by technological advancements, legal challenges, and shifting user needs. These clandestine platforms emerged as part of the broader dark web ecosystem, offering anonymity and untraceability for various transactions. Early marketplaces primarily focused on illegal goods such as illicit drugs, counterfeit documents, and weapons, facilitated by the use of anonymizing technologies like Tor and cryptocurrency payments to evade law enforcement detection. Over time, these platforms adapted to increasing scrutiny by employing sophisticated security measures and exploring new business models.
Major marketplaces have experienced varying lifespans, often characterized by periods of rapid growth followed by law enforcement crackdowns, hacking, or internal disputes leading to shutdowns. For instance, some of the most prominent marketplaces operated for several years before being dismantled, while others appeared briefly before disappearing with users’ funds. The ephemeral nature of these platforms is driven by efforts to avoid detection, the continuous evolution of security features, and the risks involved in operating such illicit sites.
Throughout their evolution, dark web marketplaces have demonstrated resilience by continuously innovating and rebranding to evade closure. This ongoing cycle of emergence and disappearance reflects the ongoing cat-and-mouse game between marketplace operators and law enforcement agencies. Despite their relatively short lifespans, these platforms have significantly influenced the landscape of online illicit trade, highlighting the importance of ongoing efforts to monitor and combat illegal activities conducted on the dark web.
Technological Advancements and Market Trends

The history and evolution of dark web marketplaces have been shaped by technological advancements and shifting market dynamics over the past two decades. These clandestine platforms emerged as a response to increasing censorship, strict regulation, and the demand for anonymous transactions. Early marketplaces primarily facilitated illegal activities such as drug trafficking and counterfeit goods, often operating on hidden services accessible via anonymizing networks like Tor. Over time, these marketplaces adopted more sophisticated security measures to protect users and evade law enforcement efforts, leading to the development of decentralized platforms that emphasized privacy and untraceability.
The technological advancements in encryption, peer-to-peer technology, and blockchain have significantly influenced the growth and resilience of these marketplaces. Innovations such as escrow services, reputation systems, and multisignature wallets have increased trust among users and reduced the risk of fraud. Additionally, the integration of cryptocurrencies as the primary mode of payment has made financial transactions more anonymous and resistant to scrutiny. As a result, dark web marketplaces have expanded their scope, offering a wider array of illegal and gray-market products, including stolen data, weapons, and hacking services.
In recent years, market trends indicate a shift towards more robust security protocols, increased use of decentralized networks, and efforts to counteract shutdowns. Marketplaces continually adapt to law enforcement techniques by migrating, innovating in platform design, or employing new technological tools to stay operational. This ongoing evolution reflects an environment where technological innovation directly influences the structure, accessibility, and resilience of dark web marketplaces. The dynamic interplay between innovation and enforcement efforts ensures that these markets remain a persistent, if clandestine, component of the broader digital ecosystem.
Operational Features of Dark Web Marketplaces
Dark web marketplaces are intricate online platforms that operate within the hidden corners of the internet, providing a range of services and products often outside the bounds of traditional commerce. These marketplaces are characterized by their unique operational features, which include anonymized transactions, encrypted communications, and decentralized infrastructure. Such features are essential to maintaining user privacy and security while navigating the illicit or sensitive goods and services offered. One notable example of such platforms is available through specialized access points, highlighting the sophisticated nature of these marketplaces. Understanding the operational features of dark web marketplaces is crucial for grasping their impact on digital security and law enforcement efforts.
User Interface and Experience
Dark web marketplaces are specialized online platforms that facilitate anonymous trading of goods and services, often operating outside the reach of traditional regulatory frameworks. These marketplaces are designed with unique operational features to maintain security, privacy, and user anonymity, which are critical for their functioning and user trust.
The user interface and experience of dark web marketplaces are tailored to prioritize simplicity and security while maintaining accessibility for users with varying levels of technical expertise. These platforms typically feature streamlined navigation, trusted transaction processes, and minimalistic design elements to reduce potential vulnerabilities. A clear layout helps users locate categories, listings, and support channels efficiently, enhancing overall usability despite the inherent complexities of operating on the dark web.
Key operational features include sophisticated encryption techniques, multi-layered authentication methods, and the use of escrow systems to secure transactions. These features help prevent fraud and protect both buyers and sellers. Additionally, marketplaces often implement strict vetting procedures for vendors and active moderation to maintain marketplace integrity.
Regarding user interface and experience, dark web marketplaces often employ:
- Encrypted communication channels to ensure privacy during interactions between users and vendors
- Simple yet secure login procedures that may involve PGP encryption or two-factor authentication
- Category-based navigation for quick access to different product or service listings
- Ratings and review systems to establish trustworthiness among users
- Automatic security alerts and context-specific help resources to assist users in navigating the platform safely
While these marketplaces prioritize user anonymity, they also seek to provide a functional and accessible environment for transactions, which requires a careful balance between security features and a user-friendly interface. This combination of operational features and user-centered design contributes to the ongoing viability of dark web marketplaces in the clandestine online economy.
Sellers and Vendor Management
Dark web marketplaces are clandestine online platforms that facilitate the exchange of goods and services outside the reach of traditional regulatory authorities. Their operational features are designed to ensure user anonymity, security, and resilience against law enforcement actions. Central to these features are the mechanisms for managing vendors and maintaining marketplace integrity, which are critical for the stability and trustworthiness of these hidden marketplaces.
One of the key operational features of dark web marketplaces is the implementation of secure and anonymous communication channels. These platforms typically employ encrypted messaging systems to facilitate interactions between buyers and vendors, preventing unauthorized interception of sensitive information. Vendor management is another core aspect, involving strict verification processes to authenticate identities and ensure the trustworthiness of sellers.
Marketplace administrators often utilize a variety of management strategies to oversee vendor activities and maintain platform security. These include the enforcement of strict rules and guidelines, regular audits, and the use of reputation systems where feedback and ratings influence vendor credibility. Additionally, multi-layered moderation, including automated monitoring and manual review, helps detect and mitigate fraudulent or malicious activity.
Operational resilience is also achieved through features such as decentralized hosting, frequent platform migrations, and the use of robust encryption protocols. These measures help evade shutdowns and reduce the risk of infiltration by law enforcement agencies. Vendor accounts are typically monitored for suspicious behavior, with automated algorithms flagging potential security threats or violations of marketplace policies.
In summary, the operation of dark web marketplaces involves sophisticated features aimed at safeguarding vendor and buyer anonymity, ensuring security, and maintaining market stability. Vendor management plays a vital role in cultivating a trustworthy environment, relying on verification, reputation systems, and vigilant oversight to sustain their clandestine economies.
Payment Systems and Cryptocurrencies
Dark web marketplaces operate within a clandestine digital environment, offering a wide range of products and services outside the reach of traditional internet censorship. These marketplaces are designed to facilitate anonymous transactions, often centered around illegal goods, through various advanced operational features. One of the most critical aspects of these platforms is their sophisticated payment systems, which enable users to conduct transactions securely and privately. Cryptocurrency integration has become the cornerstone of these payment systems, providing a decentralized and pseudonymous alternative to conventional financial services.
Dark web marketplaces typically employ a combination of security protocols and decentralized financial tools to maintain operational integrity. Prominent among these features are secure payment mechanisms that rely heavily on cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Monero, and other privacy-focused digital coins. These currencies allow users to bypass traditional banking systems, ensuring that transactions remain untraceable and confidential. The marketplaces often implement multilayered encryption, anonymized wallets, and mixing services to further enhance user privacy and prevent transaction tracing.
In addition to payment systems, these marketplaces use various operational features to sustain their clandestine environment. They include escrow services that hold funds until buyers confirm receipt of goods, multi-signature wallets for joint control over transactions, and decentralized reputation systems to establish trust among users. These features help mitigate risks and foster a secure trading environment within the dark web. Cryptocurrencies, as an integral component, enable rapid, borderless, and pseudonymous exchanges that are difficult for authorities to monitor or shut down.
Overall, the operational features of dark web marketplaces, especially their payment systems and cryptocurrency usage, demonstrate a sophisticated level of technological adaptation. These features not only support the seamless flow of illicit transactions but also contribute to the resilience and anonymity of such platforms in the face of ongoing law enforcement efforts.
Escrow and Dispute Resolution
Dark web marketplaces are specialized online platforms that facilitate the anonymous exchange of goods and services, often operating outside the scope of traditional regulatory environments. These marketplaces prioritize user privacy and security, implementing various operational features to maintain trust and functionality amidst the challenges of illicit activities. A critical aspect of their operation involves escrow services and dispute resolution mechanisms, which are essential for mitigating fraud and ensuring transaction integrity.
One of the primary operational features of these platforms is the use of escrow services. When a buyer initiates a purchase, the payment is not directly transferred to the seller. Instead, it is held securely by the marketplace’s escrow system until the buyer confirms receipt and satisfaction with the product or service. This process helps protect both parties — the buyer from receiving substandard or counterfeit goods, and the seller from non-payment after delivery. The escrow system acts as an impartial intermediary, bolstering trust within the marketplace ecosystem.

Dispute resolution is another vital operational feature for dark web marketplaces. Given the clandestine nature of transactions, conflicts may arise over product quality, delivery times, or other transaction details. To address this, marketplaces often maintain dedicated dispute resolution protocols, which may involve the platform acting as an intermediary to evaluate evidence from both parties and determine an appropriate outcome. Sometimes, external moderators or community-based arbitration processes are employed to resolve disputes, further strengthening the reliability of the marketplace.
Overall, the combination of escrow services and dispute resolution mechanisms plays a crucial role in maintaining operational integrity and user confidence in dark web marketplaces. These features enable transactions to occur securely and with greater assurance, despite the underlying risks associated with illicit commerce.
Common Activities and Listings on Dark Web Marketplaces
Dark web marketplaces are hidden online platforms where a variety of illicit and legal goods and services are bought and sold. Participants often engage in activities ranging from purchasing stolen data and illegal drugs to trading digital currencies and counterfeit goods. These marketplaces serve as digital hubs for a diverse array of transactions that are typically inaccessible through regular internet channels. For those interested in exploring these hidden networks, dark web marketplaces provide a glimpse into the complex and often clandestine world of black market trading. Understanding common activities and listings on these platforms is crucial for awareness and security purposes, as they continue to evolve and adapt to law enforcement efforts and technological changes.
Illegal Drug Sales
Dark web marketplaces are hidden online platforms where users can anonymously buy and sell various goods and services, often outside legal boundaries. These marketplaces operate on the dark web, a part of the internet not accessible through standard browsers and often accessed via specialized software that ensures user anonymity. A significant portion of the activities on these marketplaces involves illegal items, with illegal drug sales being among the most prominent and concerning issues.
Common activities on dark web marketplaces include the exchange of illegal drugs, counterfeit currency, stolen data, weapons, and hacking services. These platforms facilitate transactions using cryptocurrencies, which provide a layer of privacy and security for users. Due to the anonymous nature of the dark web, law enforcement agencies face challenges in tracking and shutting down such illegal activities.
Listings on these marketplaces frequently feature detailed descriptions, reviews, and ratings to attract customers and establish trust. The illegal drug market is particularly large, with vendors offering a variety of illicit substances such as narcotics, psychedelics, and prescription medications without prescriptions. These listings are often organized by drug type, with prices and quantities clearly displayed to facilitate quick transactions.
Common Activities on Dark Web Marketplaces
- Illegal drug sales, including marijuana, cocaine, heroin, and synthetic drugs
- Stolen data sales, such as credit card information and personal identities
- Counterfeit currencies and fake documents
- Hacking services that offer exploits, malware, and cyber-attack tools
- Sale of weapons and related accessories
- Fraudulent schemes and scams, including fake IDs and counterfeit products
The prevalence of illegal drug sales on dark web marketplaces poses serious public health and safety concerns. These platforms continue to adapt to law enforcement efforts, utilizing encryption and anonymizing technologies to maintain their operations. Understanding the common activities and listings on these marketplaces highlights the ongoing need for vigilance and effective legal responses to combat illegal online markets.
Cybercrime Services (Hacking, Ransomware)

Dark web marketplaces are clandestine platforms that facilitate the exchange of a wide range of illicit goods and services, operating outside the reach of conventional internet authorities. These marketplaces often serve as hubs for cybercriminal activities, providing a discreet environment for transactions involving illegal commodities. Common activities on these platforms include listing various illegal items such as drugs, counterfeit currency, stolen data, and weapons, creating a thriving black market economy.
Beyond illegal goods, dark web marketplaces are also known for hosting listings for cybercrime services. These services typically include hacking assistance, malware deployment, and ransomware attacks, which are marketed to individuals or organizations seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems. Such offerings tend to be detailed, with sellers advertising expertise in bypassing security measures, gaining unauthorized access, or encrypting data for monetary gain.
Cybercrime services on these platforms often encompass a range of malicious activities, including the sale of zero-day exploits, stolen credentials, and remote access tools. Ransomware, in particular, has become a prevalent tool used by cybercriminals to encrypt victim data and demand ransom payments in cryptocurrencies, providing anonymity to both the attacker and the buyer. Listings related to ransomware usually include guides or support for deploying the malware, making it accessible even to less technically skilled cybercriminals.
Engagement in such activities on dark web marketplaces poses significant threats to individuals, companies, and governments, leading to financial losses, data breaches, and operational disruptions. Law enforcement agencies worldwide actively monitor these sites to track illicit transactions and dismantle cybercrime networks, although the anonymity offered by the dark web makes enforcement challenging.
Overall, dark web marketplaces serve as focal points for a range of illegal activities, including the trading of cybercrime services. Understanding these common listings and activities is critical in developing effective cybersecurity strategies and law enforcement measures to combat digital criminal enterprises.
Counterfeit Goods and Weapons
Dark web marketplaces are clandestine platforms where users can engage in a variety of illicit activities. These sites operate within the deep web, making them less accessible and more difficult to monitor than traditional websites. Participants often utilize anonymizing tools, such as Tor, to conceal their identities and locations, which facilitates a range of illegal transactions. Among the most common activities conducted on these marketplaces are the trading of counterfeit goods and weapons, activities that pose significant legal and security risks.
Listings on dark web marketplaces frequently include:
- Counterfeit Goods: Fake currencies, SIM cards, synthetic drugs, counterfeit identification documents, and replicas of luxury items.
- Weapons: Firearms, ammunition, knives, and other dangerous tools that are illegally sold without proper regulation or oversight.
- Stolen Data: Personal information, credit card details, and login credentials obtained through hacking or data breaches.
- Illegal Substances: Illicit drugs, controlled chemicals, and unregulated pharmaceuticals.
- Fraud Services: Fake documents, hacking tools, and services for illegal activities such as hacking or scam operations.
Engaging in activities involving these listings on dark web marketplaces carries serious legal consequences and promotes dangerous behaviors. Law enforcement agencies worldwide continually work to infiltrate these sites, dismantle illegal supply chains, and shut down operations to protect public safety. Awareness of common activities and listings on such platforms is essential for understanding their risks and the importance of cybersecurity and legal compliance.
Child Exploitation Material
Dark web marketplaces are clandestine platforms that facilitate a variety of illicit activities, often hidden from public view and conventional law enforcement efforts. These marketplaces serve as hubs for managing and exchanging illegal goods and services, making them a significant concern for authorities worldwide. One of the most troubling aspects of these sites is their involvement in the distribution of harmful content, including child exploitation material. Understanding the common activities and listings on these platforms is crucial in combating their negative impact on society.
Typically, dark web marketplaces feature a range of illegal items and services, which can be broadly categorized into several key activities:
- Sale of Drugs and Controlled Substances: Many marketplaces are primarily known for drug trafficking, enabling anonymous transactions for various illegal substances.
- Weapons and Ammunition: Firearms, explosives, and other weaponry are frequently listed and sold within these environments.
- Stolen Data and Personal Information: Including credit card details, hacking tools, and compromised account credentials.
- Counterfeit Documents and Identification Cards: Fake passports, driver’s licenses, and other official documents are often available.
- Child Exploitation Material: One of the most heinous aspects involves the distribution of child abuse imagery and videos, which is strongly condemned and targeted by law enforcement agencies worldwide.
- Illicit Services: Such as hacking services, cash-out services, and illegal consulting for various criminal activities.
Listings related to child exploitation material represent a severe violation of human rights and pose significant legal and moral challenges. Law enforcement agencies worldwide continuously monitor and take action against such content to protect victims and dismantle criminal networks. Participation in or facilitation of these activities on dark web marketplaces is punishable by law and carries severe penalties.
Understanding the common activities and types of listings on dark web marketplaces is vital for developing effective strategies to combat illegal operations, especially those involving the exploitation of vulnerable populations. Ongoing efforts focus on infiltration, monitoring, and disrupting these platforms to enhance global security and safety.
Law Enforcement and Regulatory Challenges
Law enforcement agencies face significant challenges when addressing activities on the dark web, especially concerning illegal marketplaces. These hidden digital environments facilitate illicit trade, including drug trafficking, firearms sales, and other criminal endeavors, making regulation and enforcement efforts complex and resource-intensive. The anonymity provided by the dark web complicates efforts to track and apprehend offenders, requiring advanced technical skills and international cooperation. Regulating these spaces while respecting privacy rights also presents a delicate balance for authorities aiming to curb criminal activities without infringing on legitimate users. The prevalence of dark web marketplaces underscores the ongoing need for innovative strategies and collaborative approaches to combat cybercrime effectively.
Operational Security and Obfuscation Tactics
Dark web marketplaces present a complex environment that poses significant challenges for law enforcement and regulatory agencies. These platforms often operate anonymously, utilizing encryption and decentralized networks to conceal user identities and transactional activities. This inherent privacy makes it difficult to track illegal transactions involving drugs, weapons, stolen data, and other illicit goods. As a result, law enforcement agencies must employ advanced operational security measures and obfuscation tactics to conduct investigations and gather intelligence without exposing their sources or compromising ongoing operations.
One key challenge in regulating these marketplaces is their ability to rapidly adapt and employ obfuscation techniques that hinder detection efforts. Dark web marketplaces frequently change domain names, utilize layered encryption, and employ proxy servers to mask their locations. These tactics enable them to remain resilient against dismantling efforts and maintain continuous operation despite law enforcement interventions. Additionally, they often integrate anonymizing tools like Tor or VPN services, which further complicate efforts to identify operators and users involved in illegal activities.
- It’s in this underground landscape of shady buyers and sellers where dark web threats often lurk undetected until it’s too late and you suffer a breach.
- Dark web hackers often use malware such as keyloggers, ransomware, and trojan horses to access sensitive information and cause damage.
- Investigators then have the ability to filter the marketplaces by the types of goods being sold, when the marketplace was last active, and the geographies where products are being shipped to and from.
Operational security is a critical component in combatting dark web marketplaces. Agencies utilize cyber intelligence, undercover operations, and digital forensics to penetrate these encrypted environments. They also develop sophisticated algorithms and machine learning tools to analyze patterns of activity, identify counterfeit or illicit transactions, and monitor market sentiments. However, the proliferation of obfuscation tactics by marketplace operators means that law enforcement must continually innovate and adapt their strategies to stay ahead of malicious actors.
Furthermore, regulatory challenges extend beyond technical hurdles, encompassing legal and jurisdictional issues. As these marketplaces often operate across international borders, coordination among different countries’ law enforcement agencies becomes essential. International cooperation is vital to dismantling these platforms, disrupting supply chains, and prosecuting offenders. Despite these efforts, the persistent evolution of dark web marketplaces and their users’ commitment to anonymity make it a challenging landscape to regulate effectively. Continued advancements in digital investigation techniques and collaborative efforts are essential to mitigate the threats posed by these hidden networks.
Investigation Techniques and Technologies
Dark web marketplaces have emerged as complex environments that pose significant challenges for law enforcement and regulatory agencies worldwide. Their anonymous and decentralized nature makes it difficult to track illicit activities, including drug trafficking, illegal arms sales, and cybercrime. To combat these threats, authorities employ a combination of advanced investigation techniques and emerging technologies designed to uncover and disrupt illegal operations while respecting legal boundaries and privacy considerations.
Investigation methods tailored for dark web environments often include digital forensics and cyber intelligence gathering. Investigators utilize specialized tools to analyze metadata, monitor transaction patterns, and identify potential links between vendors and buyers. Undercover operations and collaboration with international agencies enhance the capability to infiltrate dark web marketplaces and gather critical intelligence.
Technologies such as Tor (The Onion Router) facilitate anonymity for users accessing dark web marketplaces, but they also present hurdles for law enforcement. To overcome these, authorities leverage techniques like traffic analysis, network infiltration, and the use of lawfully obtained malware to de-anonymize users and trace transactions. Additionally, machine learning algorithms and data analytics enable the identification of suspicious behaviors and fraud detection, aiding in the rapid response to emerging threats.
Despite these technological advancements, challenges persist in balancing proactive enforcement with the protection of digital rights. Developing effective regulatory frameworks requires continuous adaptation, cross-jurisdictional cooperation, and investment in innovative investigation tools. Ultimately, addressing the complexities of dark web marketplaces demands a nuanced approach that combines technical expertise, legal authority, and international collaboration to prevent and combat illegal online activities.
Examples of Market Takedowns and Disruptions
Dark web marketplaces have emerged as clandestine platforms that facilitate the exchange of illegal goods and services, posing significant challenges for law enforcement and regulatory authorities worldwide. These marketplaces operate on the anonymized and encrypted layers of the internet, making detection and investigation complex and resource-intensive. Governments and agencies often employ sophisticated cyber forensics, undercover operations, and international cooperation to combat illicit activities on these platforms.
One notable example of market takedowns involved coordinated efforts across multiple countries to shut down major dark web marketplaces suspected of facilitating drug trafficking, weapons trading, and other criminal enterprises. These operations often begin with infiltration, data collection, and surveillance to identify key vendors and administrators. Once enough intelligence is gathered, authorities execute dismantling actions by seizing servers, arresting individuals involved, and restoring regulatory oversight to prevent the resurgence of illegal marketplaces.
Disruptions in the dark web marketplace ecosystem also include technological interventions such as backend shutdowns, seizure of cryptocurrency accounts, and disruption of anonymizing services that support these platforms. These measures significantly diminish the operational capacity of illicit marketplaces, impacting the supply chains and access to illegal goods. Despite these efforts, the persistent adaptation of marketplace operators, including shifting to more resilient decentralized platforms, underscores the ongoing cat-and-mouse game faced by law enforcement agencies.
Tools and Techniques for Disruption
Tools and techniques for disruption are essential for navigating complex environments and overcoming challenges across various sectors. In particular, understanding how to effectively identify and counteract illicit activities on the dark web has become increasingly important. Dark web marketplaces serve as hubs for a wide range of unlawful transactions, making them a focal point for law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals aiming to disrupt criminal networks. Employing specialized tools and strategic methods can help authorities and researchers gain insights, monitor activities, and implement measures to dismantle these covert operations.
Blockchain Analytics and Intelligence
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital security, tools and techniques for disruption play a critical role in combatting illicit activities on dark web marketplaces. Leveraging advanced blockchain analytics and intelligence, agencies and organizations can track transactions, identify malicious actors, and disrupt illegal operations effectively. These technologies enable a deeper understanding of blockchain transactions, helping to uncover patterns and linkages that are otherwise hidden in the opaque environment of the dark web.
Blockchain analytics tools are essential for monitoring cryptocurrency flows, which are often used for illicit transactions on dark web marketplaces. These tools analyze transaction data to identify suspicious patterns, trace the origins and destinations of funds, and connect various wallets to known criminal entities. By providing real-time insights, these analytics enhance the ability to intercept illicit financial flows before they are utilized for illegal activities.
Advanced intelligence techniques involve the integration of data from multiple sources, including open and dark web monitoring, to create a comprehensive picture of ongoing malicious activities. Machine learning algorithms can detect anomalies and predict potential threats based on historical data. Such methods are vital in identifying emerging threats within dark web marketplaces, where anonymity is often exploited to hide illegal dealings.
The combination of blockchain analytics and intelligence tools supports law enforcement efforts and cybersecurity initiatives aimed at disrupting criminal networks operating on dark web marketplaces. Through these technologies, authorities can build cases, track illicit funding, and ultimately dismantle networks involved in drug trafficking, fraud, and other illegal enterprises. Overall, the ongoing development and application of these tools are essential for maintaining security and integrity in the digital space.
Financial Institution Collaboration
Disruption in financial services often requires innovative tools and collaborative techniques to effectively counteract illegal activities, including those occurring on dark web marketplaces. Financial institutions are increasingly adopting advanced technological solutions and forging strategic partnerships to enhance security measures, detect fraudulent activities, and prevent money laundering. Utilizing sophisticated data analytics and artificial intelligence can help identify patterns associated with illicit transactions, enabling quicker responses and proactive prevention. Additionally, collaboration among banks, law enforcement agencies, and cybersecurity firms fosters a united front against financial crimes linked to the dark web marketplaces.
One key technique is the deployment of real-time transaction monitoring systems that leverage machine learning algorithms to flag suspicious activities that may involve black market transactions. These tools can analyze large volumes of data to detect anomalies indicative of unauthorized or illegal financial flows. Cyber intelligence sharing platforms also play a crucial role by providing valuable insights into emerging threats and tactics used by cybercriminals. This collective intelligence enhances the ability of institutions to stay ahead of malicious actors involved in maintaining dark web marketplaces.
Furthermore, collaborative efforts extend to international cooperation, where cross-border information exchange and joint investigations are instrumental in dismantling networks facilitating illegal trade. Financial institutions often participate in industry-led initiatives to standardize best practices, improve compliance measures, and promote transparency. Training personnel to recognize signs of illicit activity and adopting robust cybersecurity protocols remain vital components of a comprehensive strategy against the misuse of financial channels associated with dark web marketplaces.
In summary, the combination of advanced tools like AI-driven detection systems and the power of collaborative techniques across sectors forms the backbone of effective disruption strategies targeting illegal activities linked to dark web marketplaces. Maintaining vigilance and fostering cooperation are essential to safeguarding the integrity of the financial ecosystem against evolving cyber threats.
Monitoring and Blocking Illicit Transactions
Addressing the challenges posed by illegal activities on dark web marketplaces requires a combination of innovative tools and strategic techniques designed to disrupt, monitor, and block illicit transactions. These platforms often facilitate the exchange of illegal goods and services, making it essential for authorities and cybersecurity professionals to stay ahead of evolving methods used by cybercriminals.
One of the primary tools used in combating illicit transactions is advanced data analysis software, which helps identify patterns and anomalies indicative of illegal activities. These tools can analyze large volumes of transaction data, user behaviors, and communication patterns to flag suspicious activities for further investigation. Machine learning models are particularly effective in detecting emerging threats by continuously learning from new data and adapting their detection capabilities.
Monitoring techniques often involve the deployment of darknet crawling and surveillance tools that systematically scan dark web marketplaces for illicit listings and relevant communications. These tools gather intelligence on vendors, transaction volumes, and changing marketplace structures. Additionally, custom algorithms can be employed to trace cryptocurrency transactions, which are frequently used for payments due to their pseudonymous nature. Blockchain analysis tools enable investigators to follow the flow of funds, linking transactions to known entities or patterns associated with criminal activity.
Blocking illicit transactions relies heavily on identifying and disrupting the infrastructure that supports these activities. This can include takedown operations aimed at shutting down marketplaces, as well as targeting payment processors or cryptocurrency exchangers that facilitate illegal transactions. Implementing multi-layered monitoring systems allows organizations to intercept suspicious transactions early, preventing funds from being transferred or laundered further.
Collaboration between law enforcement agencies, private cybersecurity firms, and financial institutions is vital to enhance the effectiveness of these tools and techniques. By sharing intelligence and leveraging diverse expertise, efforts to detect, disrupt, and block illicit transactions on dark web marketplaces can be significantly improved, contributing to a safer online environment and reducing the profitability of illegal trade.
Seizure of Infrastructure and Funds
Dark web marketplaces are often targeted by various tools and techniques aimed at disrupting their operations, seizing infrastructure, and intercepting funds. Law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity organizations employ a combination of technical measures and strategic methods to undermine the anonymity and accessibility of these illicit platforms. Such approaches are essential in disrupting illegal trade and dismantling criminal networks operating within the dark web.
One primary technique involves the use of network infiltration tools designed to identify and monitor activity on dark web marketplaces. These tools often utilize traffic analysis, pattern recognition, and behavioral analytics to trace transactions and pinpoint the location of servers hosting illegal content. Additionally, infiltration through undercover operations and digital surveillance helps authorities gather intelligence and build cases against operators of these hidden marketplaces.
Seizing infrastructure is another critical step in disrupting dark web activities. This may involve server shutdowns, takedown operations, and the deployment of malware to disable or control compromised systems. Law enforcement agencies often collaborate with internet service providers and hosting companies to identify and seize servers hosting illicit marketplaces, effectively cutting off their online presence. Cyberattack techniques such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are also employed to disable access to these platforms temporarily or permanently.
Intercepting funds is a vital aspect of combating illegal online markets. Financial tracing and blockchain analysis tools enable authorities to follow cryptocurrency transactions associated with dark web marketplaces. Since these platforms typically handle payments via cryptocurrencies, advanced de-anonymization techniques can link wallet addresses to real-world identities. Freezing or seizure of funds requires coordination with financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges to prevent further transactions and disrupt the financial flow of these operations.
Overall, the fight against illegal dark web marketplaces involves an integrated approach combining technical disruption, infrastructure seizure, and financial interdiction. These tools and techniques continue to evolve, reflecting the dynamic nature of cybercriminal tactics and the ongoing efforts of law enforcement agencies worldwide to combat illicit online activity.